What Is Wireshark Used For
Wireshark Tutorial

What is Wireshark?
Wireshark is an open-source packet analyzer, which is used for pedagogy, analysis, software development, advice protocol development, and network troubleshooting.
Information technology is used to track the packets and then that each 1 is filtered to meet our specific needs. It is commonly called every bit a sniffer, network protocol analyzer, and network analyzer. It is too used past network security engineers to examine security problems.
Wireshark is a complimentary to utilise application which is used to apprehend the data back and forth. It is often chosen as a free packet sniffer computer application. It puts the network menu into an unselective mode, i.east., to take all the packets which it receives.
Uses of Wireshark:
Wireshark tin be used in the following ways:
- It is used by network security engineers to examine security problems.
- It allows the users to scout all the traffic being passed over the network.
- It is used past network engineers to troubleshoot network problems.
- It also helps to troubleshoot latency issues and malicious activities on your network.
- It can also analyze dropped packets.
- It helps us to know how all the devices like laptop, mobile phones, desktop, switch, routers, etc., communicate in a local network or the balance of the world.
What is a parcel?
A packet is a unit of data which is transmitted over a network between the origin and the destination. Network packets are small-scale, i.e., maximum 1.5 Kilobytes for Ethernet packets and 64 Kilobytes for IP packets. The data packets in the Wireshark can be viewed online and can be analyzed offline.
History of Wireshark:
In the late 1990's Gerald Combs, a computer science graduate of the University of Missouri-Kansas Urban center was working for the small Internet access provider (Internet access provider). The protocol at that time did not consummate the chief requirements. So, he started writing ethereal and released the beginning version around 1998. The Network integration services owned the Ethernet trademark.
Combos still held the copyright on most of the ethereal source lawmaking, and the rest of the source lawmaking was re-distributed under the GNU GPL. He did not ain the Ethereal trademark, so he inverse the name to Wireshark. He used the contents of the ethereal every bit the basis.
Wireshark has won several manufacture rewards over the years including eWeek, InfoWorld, PC Magazine and besides every bit a elevation-rated packet sniffer. Combos continued the piece of work and released the new version of the software. There are around 600 contributed authors for the Wireshark production website.
Functionality of Wireshark:
Wireshark is similar to tcpdump in networking. Tcpdump is a common packet analyzer which allows the user to display other packets and TCP/IP packets, being transmitted and received over a network attached to the reckoner. It has a graphic end and some sorting and filtering functions. Wireshark users can come across all the traffic passing through the network.
Wireshark can besides monitor the unicast traffic which is not sent to the network's MAC accost interface. But, the switch does non pass all the traffic to the port. Hence, the promiscuous mode is not sufficient to see all the traffic. The various network taps or port mirroring is used to extend capture at whatever signal.
Port mirroring is a method to monitor network traffic. When it is enabled, the switch sends the copies of all the network packets present at one port to another port.
What is color coding in Wireshark?
The packets in the Wireshark are highlighted with blue, black, and greenish color. These colors assistance users to place the types of traffic. It is also called as bundle colorization. The kinds of coloring rules in the Wireshark are temporary rules and permanent rules.
- The temporary rules are at that place until the program is in active style or until we quit the plan.
- The permanent colour rules are available until the Wireshark is in utilise or the adjacent time you run the Wireshark. The steps to utilise color filters volition be discussed subsequently in this topic.
Features of Wireshark
- It is multi-platform software, i.e., it can run on Linux, Windows, OS X, FreeBSD, NetBSD, etc.
- Information technology is a standard three-pane package browser.
- It performs deep inspection of the hundreds of protocols.
- Information technology often involves alive analysis, i.e., from the different types of the network similar the Ethernet, loopback, etc., nosotros can read live data.
- It has sort and filter options which makes ease to the user to view the data.
- It is besides useful in VoIP analysis.
- Information technology can likewise capture raw USB traffic.
- Various settings, like timers and filters, can be used to filter the output.
- Information technology can only capture parcel on the PCAP (an application programming interface used to capture the network) supported networks.
- Wireshark supports a variety of well-documented capture file formats such as the PcapNg and Libpcap. These formats are used for storing the captured data.
- Information technology is the no.one slice of software for its purpose. It has endless applications ranging from the tracing down, unauthorized traffic, firewall settings, etc.
Installation of Wireshark Software
Below are the steps to install the Wireshark software on the computer:
- Open up the web browser.
- Search for 'Download Wireshark.'
- Select the Windows installer co-ordinate to your system configuration, either 32-bt or 64-chip. Save the programme and close the browser.
- Now, open the software, and follow the install pedagogy by accepting the license.
- The Wireshark is ready for use.
On the network and Cyberspace settings pick, we can bank check the interface connected to our estimator.
If you are Linux users, then you will find Wireshark in its package repositories.
Past selecting the current interface, nosotros can become the traffic traversing through that interface. The version used hither is three.0.3. This version will open equally:
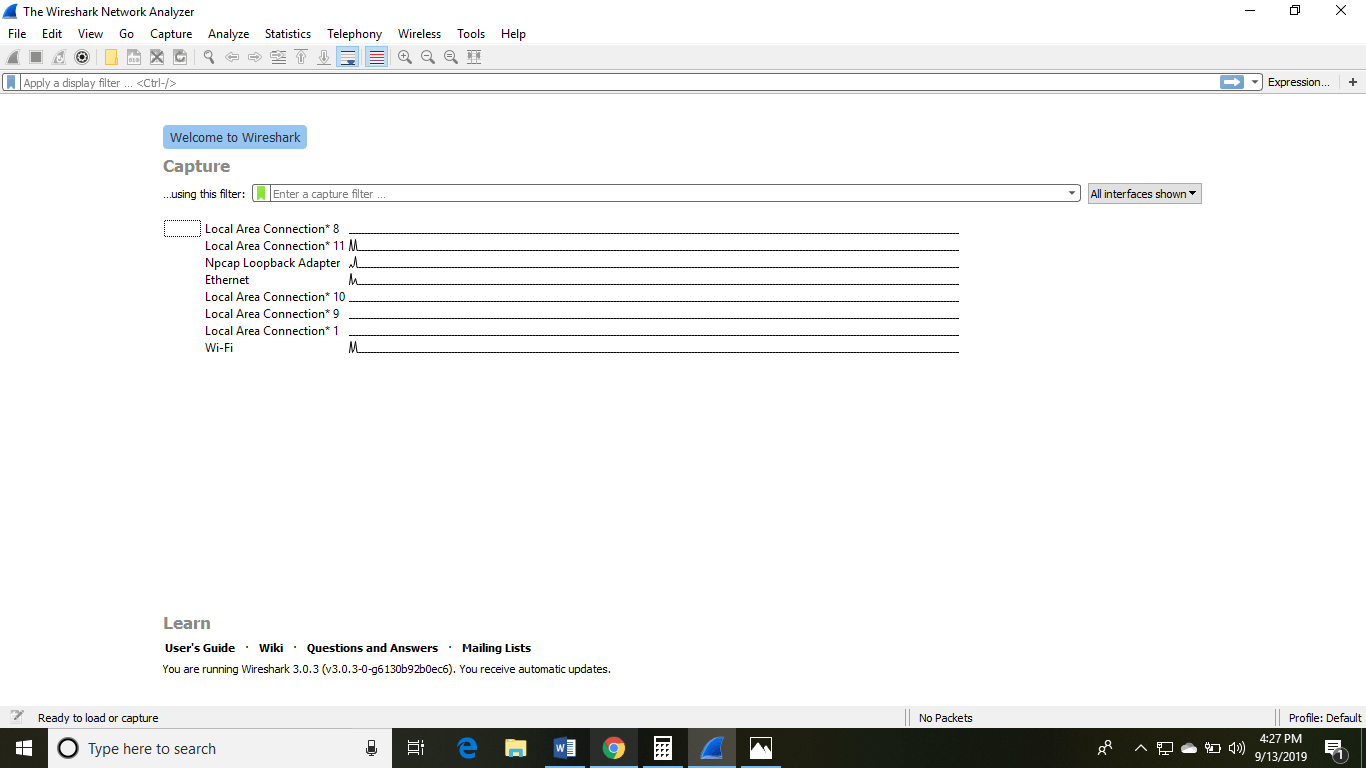
The Wireshark software window is shown above, and all the processes on the network are carried inside this screen only.
The options given on the list are the Interface list options. The number of interface options volition be present. Selection of any selection will make up one's mind all the traffic. For example, from the above fig. select the Wi-Fi option. Later this, a new window opens upwards, which will evidence all the current traffic on the network. Below is the image which tells u.s. about the alive capture of packets and our Wireshark will wait like:
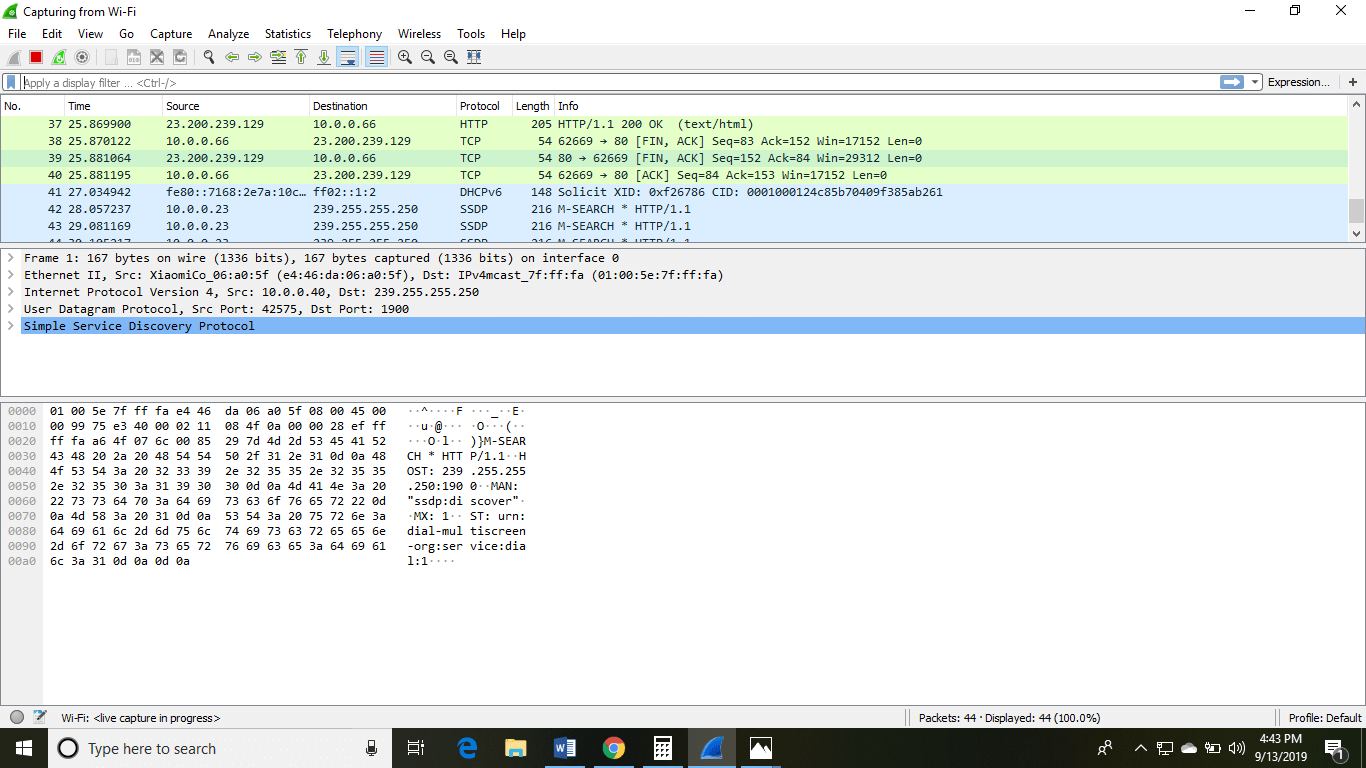
The above arrow shows the packet content written in hexadecimal or the ASCII format. And the data above the packet content, are the details of the package header.
It will continue listening to all the information packets, and you will get much data. If you lot want to meet a particular data, then you can click on the red button. The traffic will be stationary, and you can note the parameters like time, source, destination, the protocol existence used, length, and the Info. To view in-depth detail, you tin can click on that item address; a lot of the information will exist displayed below that.
There will exist detailed information on HTTP packets, TCP packets, etc. The red button is shown below:
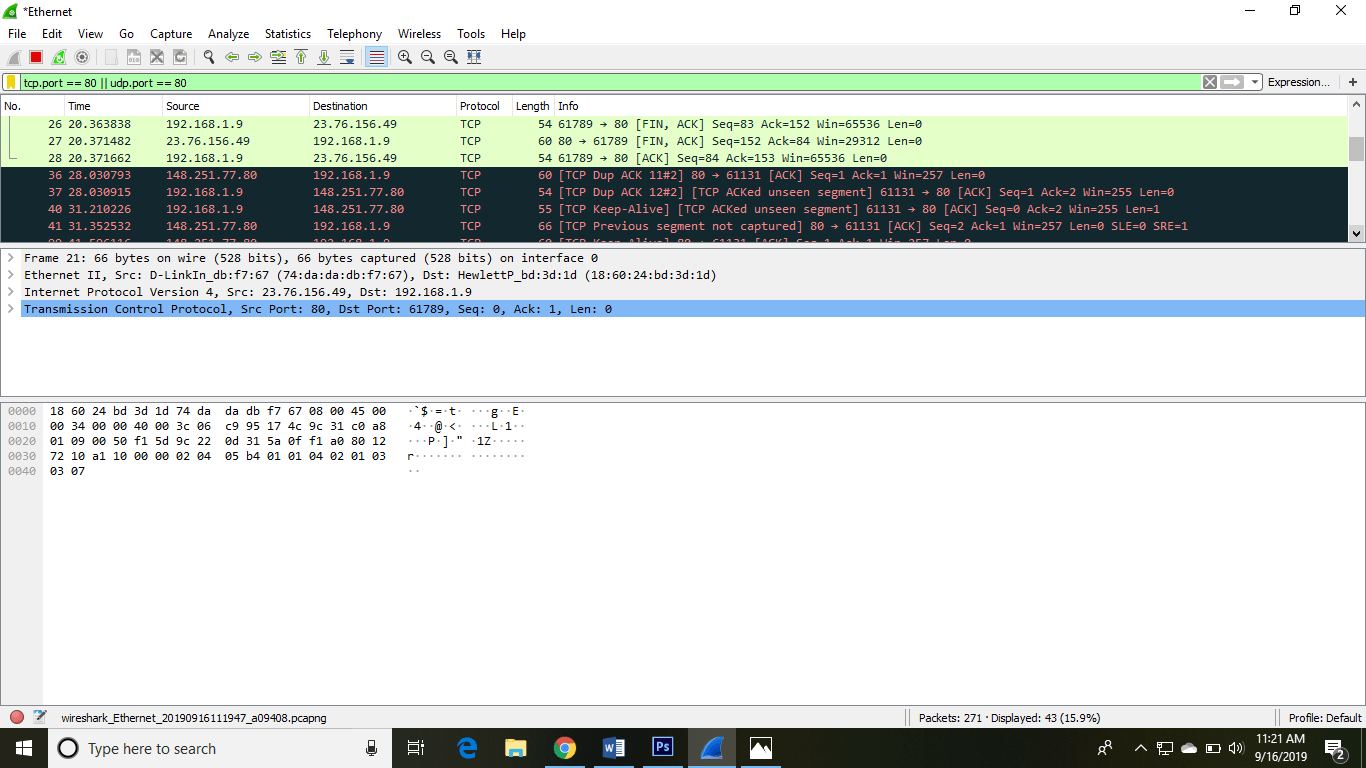
The screen/interface of the Wireshark is divided into 5 parts:
- Showtime office contains a card bar and the options displayed below it. This part is at the top of the window. File and the capture menus options are ordinarily used in Wireshark. The capture menu allows to start the capturing process. And the File menu is used to open and salve a capture file.
- The second office is the packet listing window. It determines the packet flow or the captured packets in the traffic. It includes the parcel number, time, source, destination, protocol, length, and info. We can sort the parcel listing past clicking on the column name.
- Side by side comes the package header- detailed window. It contains detailed information near the components of the packets. The protocol info can too be expanded or minimized according to the information required.
- The bottom window called the packet contents window, which displays the content in ASCII and hexadecimal format.
- At concluding, is the filter field which is at the top of the display. The captured packets on the screen can be filtered based on whatever component according to your requirements. For example, if we want to see only the packets with the HTTP protocol, we tin can apply filters to that pick. All the packets with HTTP as the protocol will merely be displayed on the screen, shown below:
You lot can also select the connection to which your calculator is connected. For example, in this PC, we have chosen the electric current network, i.e., the ETHERNET.
After connecting, you lot can picket the traffic beneath:
In view option on the menu bar, we can also change the view of the interface. You lot can alter the number of things in the view menu. You can also enable or disable any pick according to the requirements.
There is a filter cake below the menu bar, from where a large amount of data can be filtered. For example, if we apply a filter for HTTP, only the interfaces with the HTTP volition be listed.
If you want to filter co-ordinate to the source, right-click on the source you desire to filter and select 'Utilize as Filter' and choose '...and filter.'
Steps for the permanent colorization are: click on the 'View' pick on the menu bar and select 'Coloring Rules.' The table will appear like the paradigm shown below:
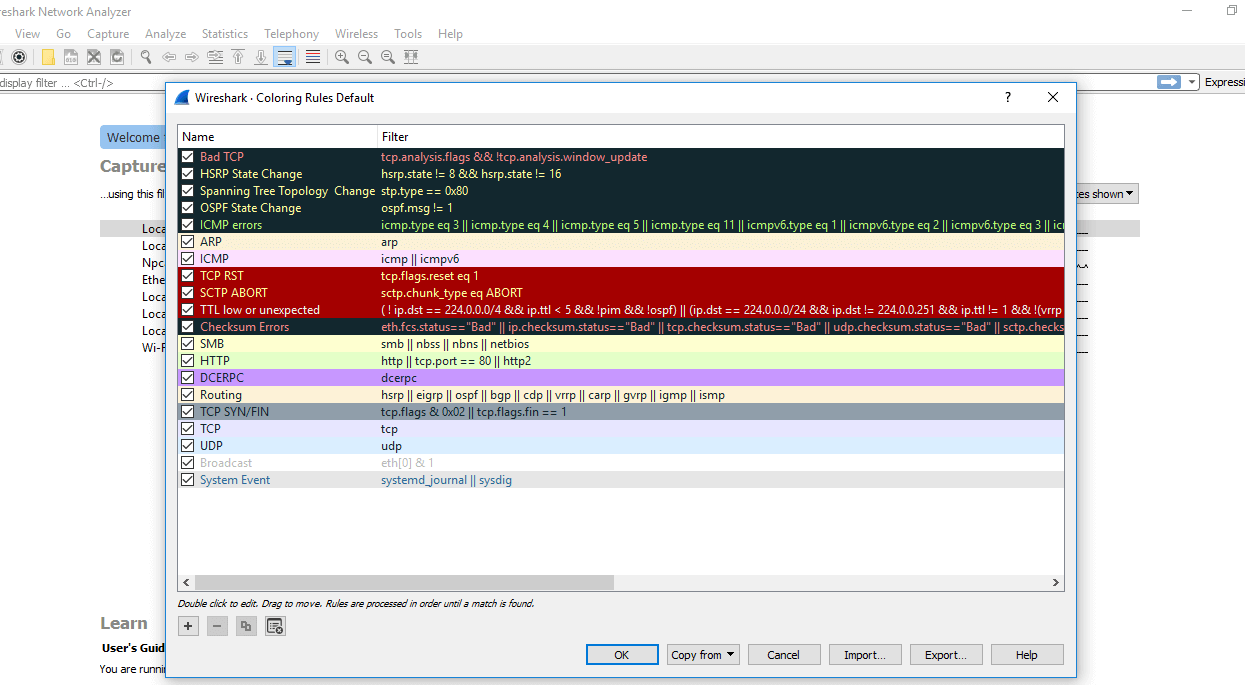
For the network administrator job, advanced noesis of Wireshark is considered as the requirements. So, it is essential to empathise the concepts of the software. It contains these 20 default coloring rules which tin can be added or removed according to the requirements.
Select the choice 'View' and then choose 'Colorize Bundle Listing,' which is used to toggle the color on and off.
Notation: If you are non sure about the version of your desktop or the laptop, and so you can download the 32-bit Wireshark which will run about 99% on every type of computers
Now let's start with this nuts-
Bones concepts of the Network Traffic
IP Addresses: It was designed for the devices to communicate with each other on a local network or over the Internet. Information technology is used for host or network interface identification. Information technology provides the location of the host and capacity of establishing the path to the host in that network. Net Protocol is the ready of predefined rules or terms under which the communication should exist conducted. The types of IP addresses are IPv4 and IPv6.
- IPv4 is a 32-bit address in which each group represents 8 bits ranging from 0 to 255.
- IPv6 is a 128-bit address.
IP addresses are assigned to the host either dynamically or static IP accost. Nigh of the individual users have dynamic IP accost while business concern users or servers accept a static IP address. Dynamic accost changes whenever the device is continued to the Internet.
Computer Ports: The estimator ports work in combination with the IP address directing all approachable and incoming packets to their proper places. There are well-known ports to work with like FTP (File Transfer Protocol), which has port no. 21, etc. All the ports take the purpose of directing all packets in the predefined management.
Protocol: The Protocol is a set of predefined rules. They are considered as the standardized way of communication. I of the virtually used protocol is TCP/IP. It stands for Transmission Control Protocol/ Cyberspace Protocol.
OSI model: OSI model stands for Open up Organization Interconnect. OSI model has seven layers, namely, Awarding layer, Presentation layer, Session layer, Transport layer, Network layer, Information link layer, and the concrete layer. OSI model gives a particular representation and explanation of the manual and reception of data through the layers. OSI model supports both connectionless and connection-oriented communication manner over the network layer. The OSI model was developed by ISO (International Standard Arrangement).
Most used Filters in Wireshark
Whenever we blazon whatever commands in the filter control box, information technology turns green if your command is correct. It turns red if information technology is incorrect or the Wireshark does not recognize your command.
Below is the list of filters used in Wireshark:
| Filters | Description |
|---|---|
| ip.addr Instance- ip.addr==10.0.10.142 ip.src ip.dst | It is used to specify the IP address as the source or the destination. This example volition filter based on this IP accost as a source and a destination. If we want for a detail source or destination then, Information technology is used for the source filter. It is used for the destination. |
| protocol Example- dns or http 'Dns and http' is never used. | This command filters based on the protocol. It requires the packet to be either dns protocol or http protocol and volition display the traffic based on this. We would non use the command 'dns and http' considering it requires the package to be both, dns too as http, which is incommunicable. |
| tcp.port Example: tcp.port==443 | Information technology sets filter based on the specific port number. It volition filter all the packets with this port number. |
| 4. udp.port | It is same as tcp.port. Instead, udp is used. |
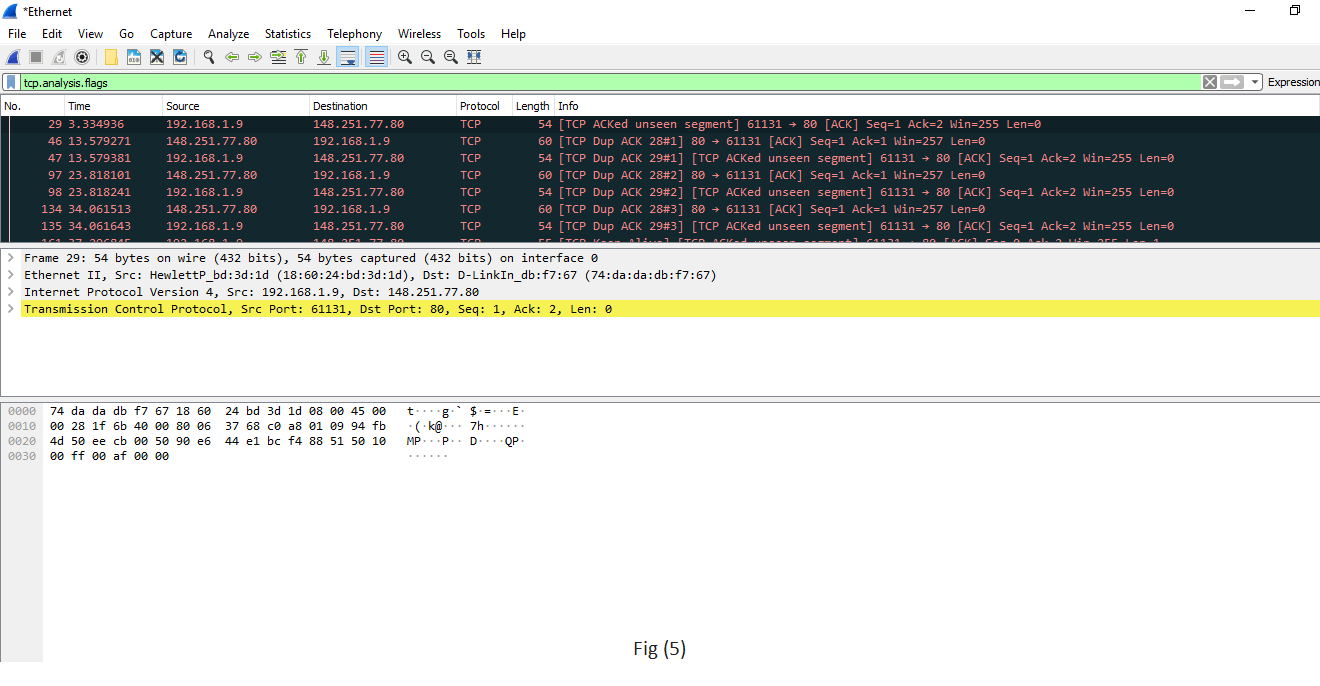
| tcp.assay.flags example is shown in fig(5). | Wireshark tin can flag TCP problems. This command will only display the bug that Wireshark identifies. Case, packet loss, tcp segment not captured, etc. are some of the problems. Information technology chop-chop identifies the problem and is widely used. |
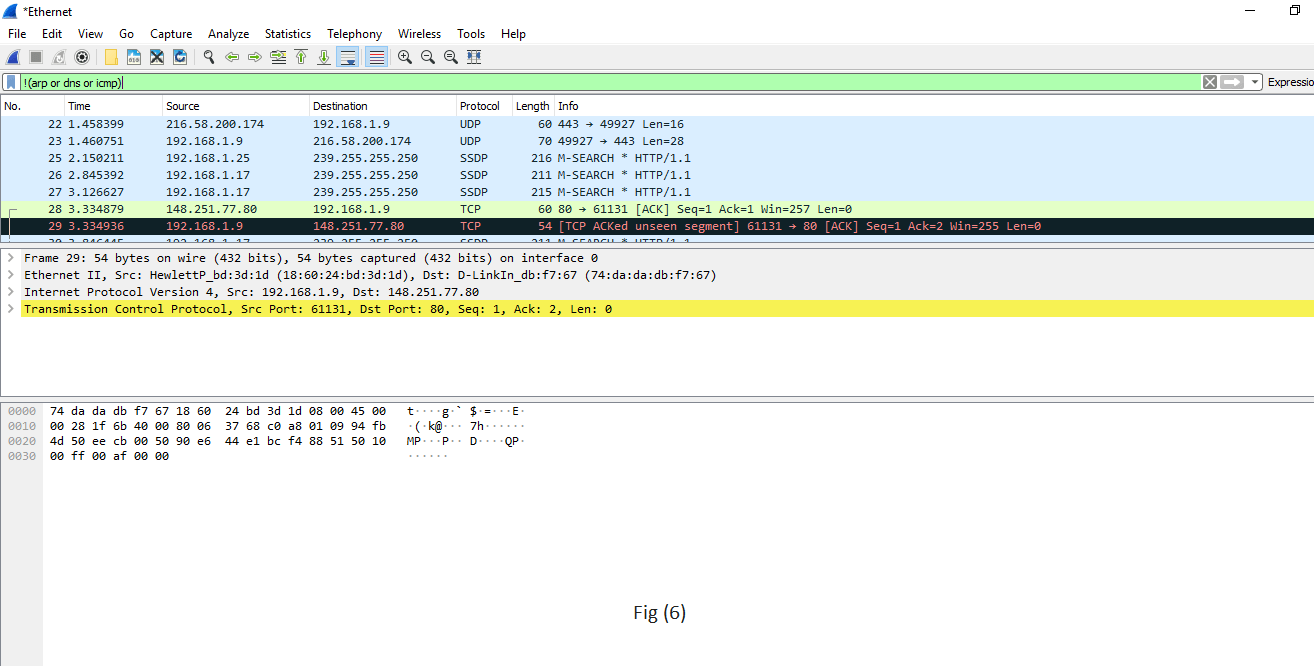
| 6.!() For example, !(arp or dns or icmp) This is shown in fig (half dozen). | It is used to filter the list of protocols or applications, in which nosotros are not interested. It will remove arp, dns, and icmp, and only the remaining will be left or it clean the things that may non be helpful. |
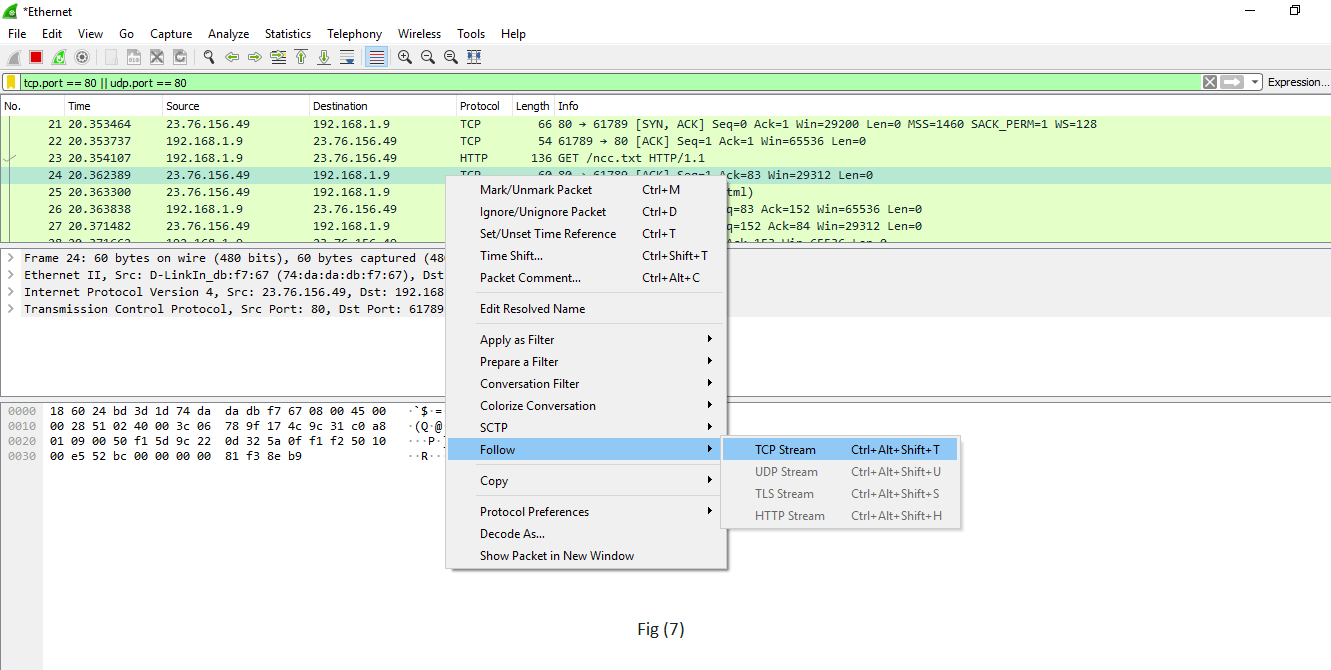
| Select any packet. Right-click on information technology and select 'Follow' and then select' TCP stream.' Shown in fig. (vii). | It is used if you desire to work on a single connectedness on a TCP chat. Anything related to the single TCP connection will exist displayed on the screen. |
| tcp contains the filter For instance- tcp contains Facebook Or udp contains Facebook | It is used to display the packets which contain such words. In this, Facebook word in any packet in this trace file i.due east., finding the devices, which are talking to Facebook. This command is useful if you are looking for a username, word, etc. |
| http.asking For the responses or the response code, y'all can type http.response.code==200 | It will display all the http requests in the trace file. You can meet all the servers, the client is involved. |
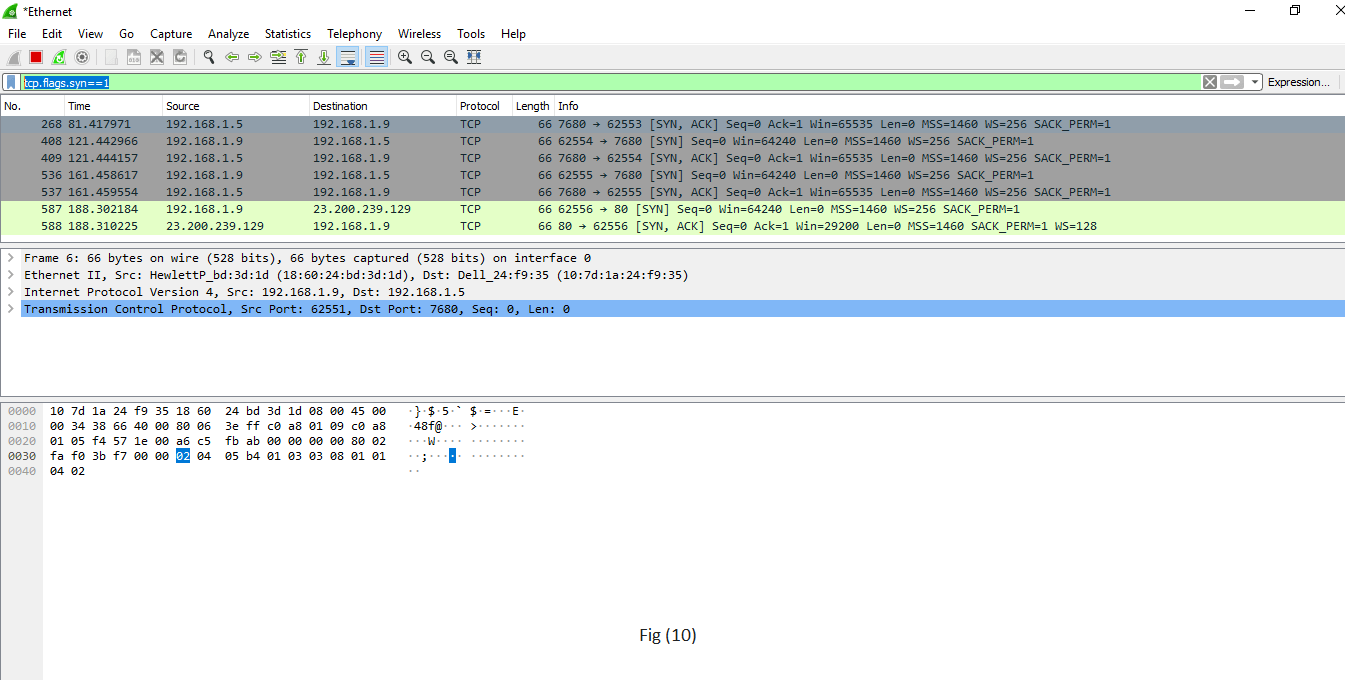
| tcp.flags.syn==1 This is shown in fig (10). tcp.flags.reset | This will display all the packets with the sync congenital-in tcp header prepare to 1. This volition show all the packets with tcp resets. |
Wireshark packet sniffing
Wireshark is a parcel sniffing plan that administrators can use to isolate and troubleshoot problems on the network. It tin as well be used to capture sensitive data similar usernames and passwords. Information technology tin can too exist used in wrong style (hacking) to ease driblet.
Packet sniffing is defined equally the process to capture the packets of information flowing across a figurer network. The Packet sniffer is a device or software used for the process of sniffing.
Below are the steps for bundle sniffing:
- Open the Wireshark Awarding.
- Select the current interface. Hither in this example, interface is Ethernet that nosotros would be using.
- The network traffic will be shown below, which will be continuous. To stop or watch any particular bundle, y'all tin can printing the cherry push below the menu bar.
Utilise the filter by the proper noun 'http.' After the filter is applied, the screen will look every bit:
The in a higher place screen is blank, i.e.; there is no network traffic equally of now.
Open up the browser. In this example, we have opened the 'Net Explorer.' You tin can cull any browser.
Every bit soon as we open the browser, and type any address of the website, the traffic will start showing, and exchange of the packets volition as well offset. The image for this is shown below:
The above process explained is called equally packet sniffing.
Username and password sniffing
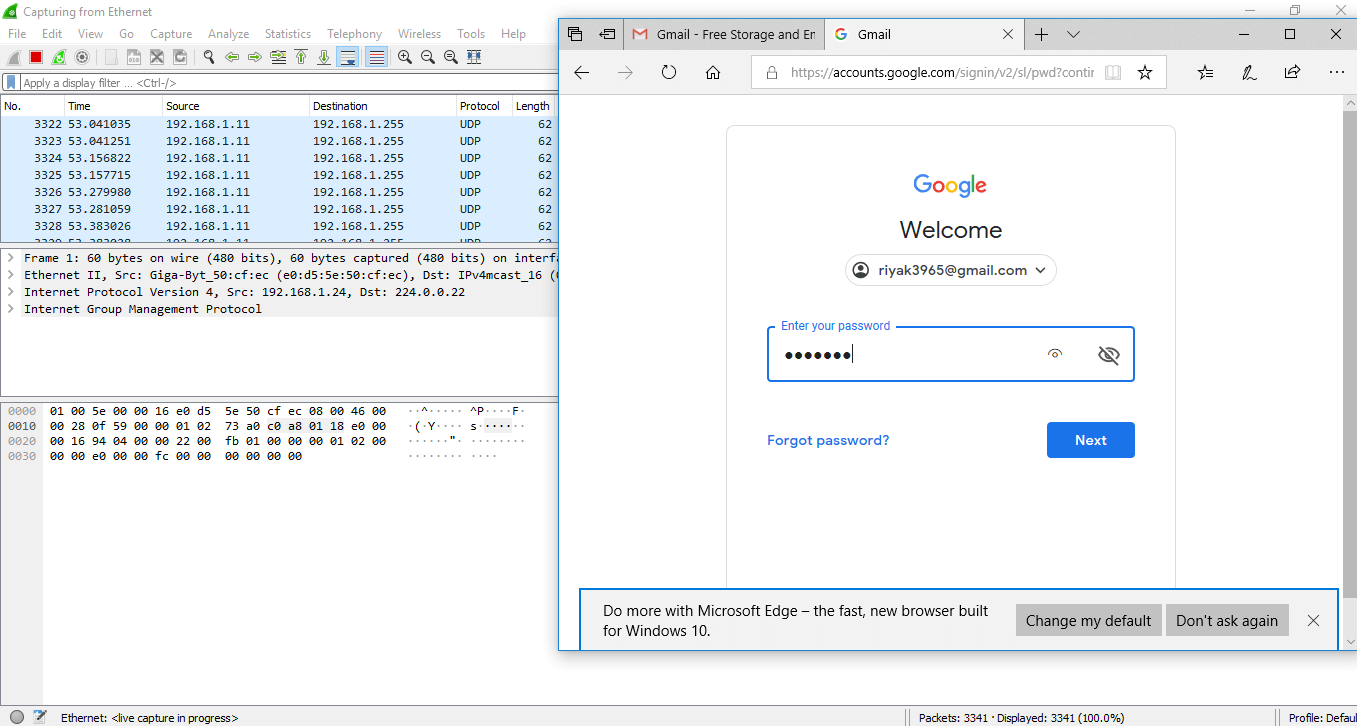
Information technology is the process used to know the passwords and username for the item website. Let'southward take an case of gmail.com. Below are the steps:
- Open up the Wireshark and select the suitable interface.
- Open up the browser and enter the web address. Here, nosotros have entered gmail.com, which is highly secured. Enter your e-mail address and the password. The epitome is shown below:
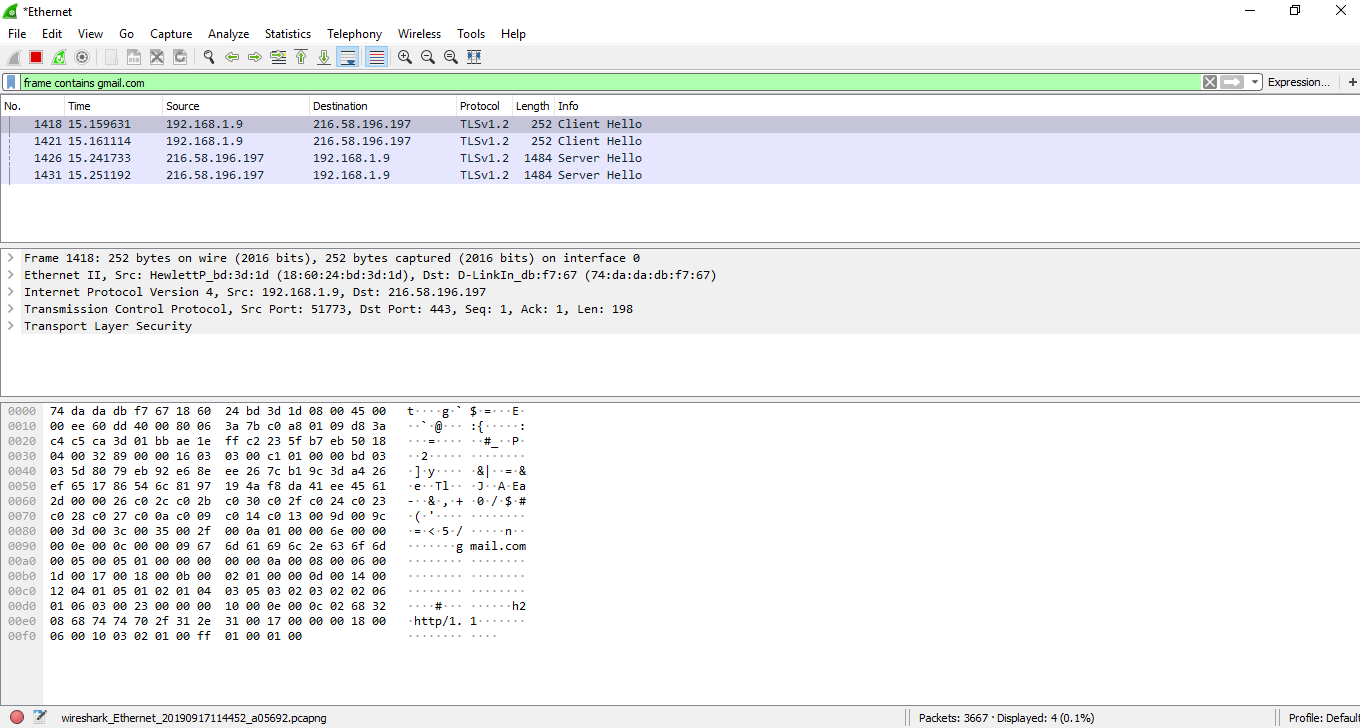
- Now, go to the Wireshark and on the filters block, enter 'frame contains gmail.com.' Then y'all can see some traffic.
- Correct-click on the particular network and select 'Follow', and and then 'TCP Stream.' You tin can see that all the data is secured in the encrypted form.
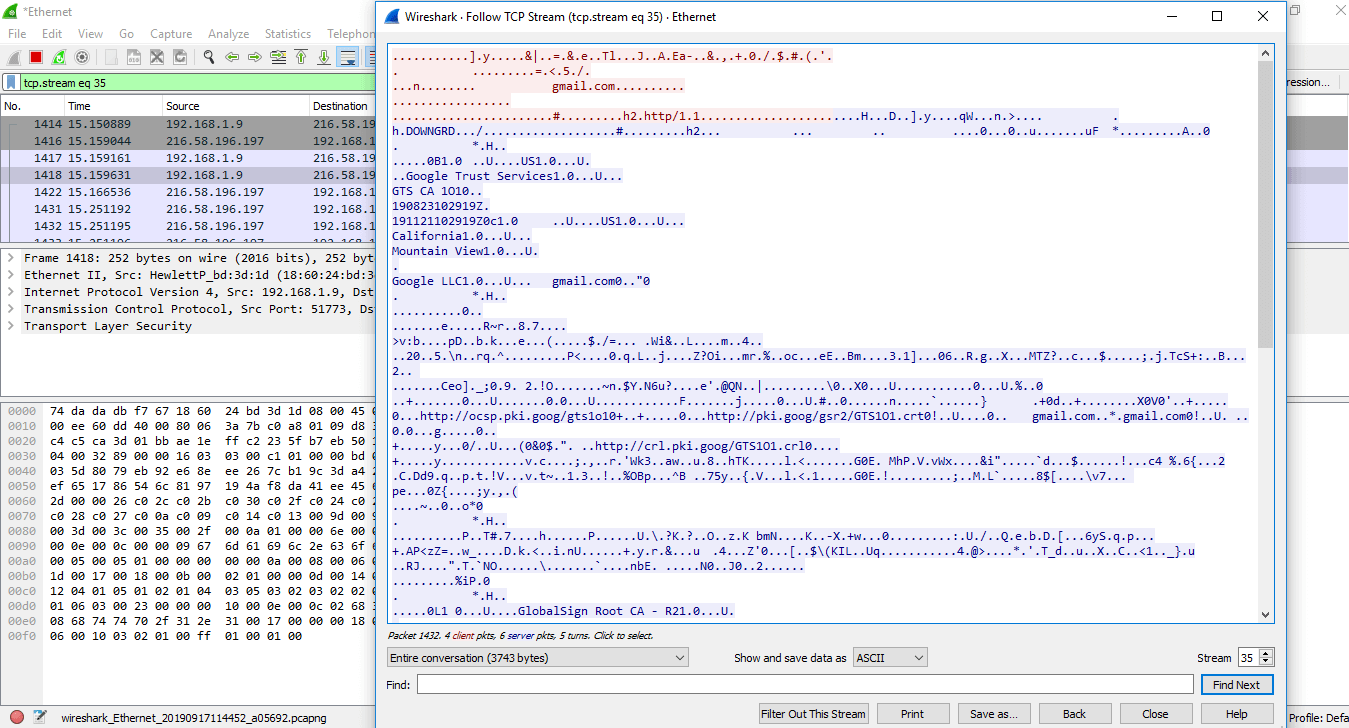
In the arrow shown in a higher place, the 'show and salve information as' has many choices. These options are- ASCII, C Arrays, EBCDIC (Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange Lawmaking), etc. EBCDIC is used in mainframe and mid-range IBM figurer operating systems.
Wireshark Statistics
The Wireshark provides a wide domain of statistics. They are listed below:
Below is the list of statistics of Wireshark along with the clarification:
| Capture file properties | It includes file, time, capture, interfaces (current interface in use), and Statistics (measurements). |
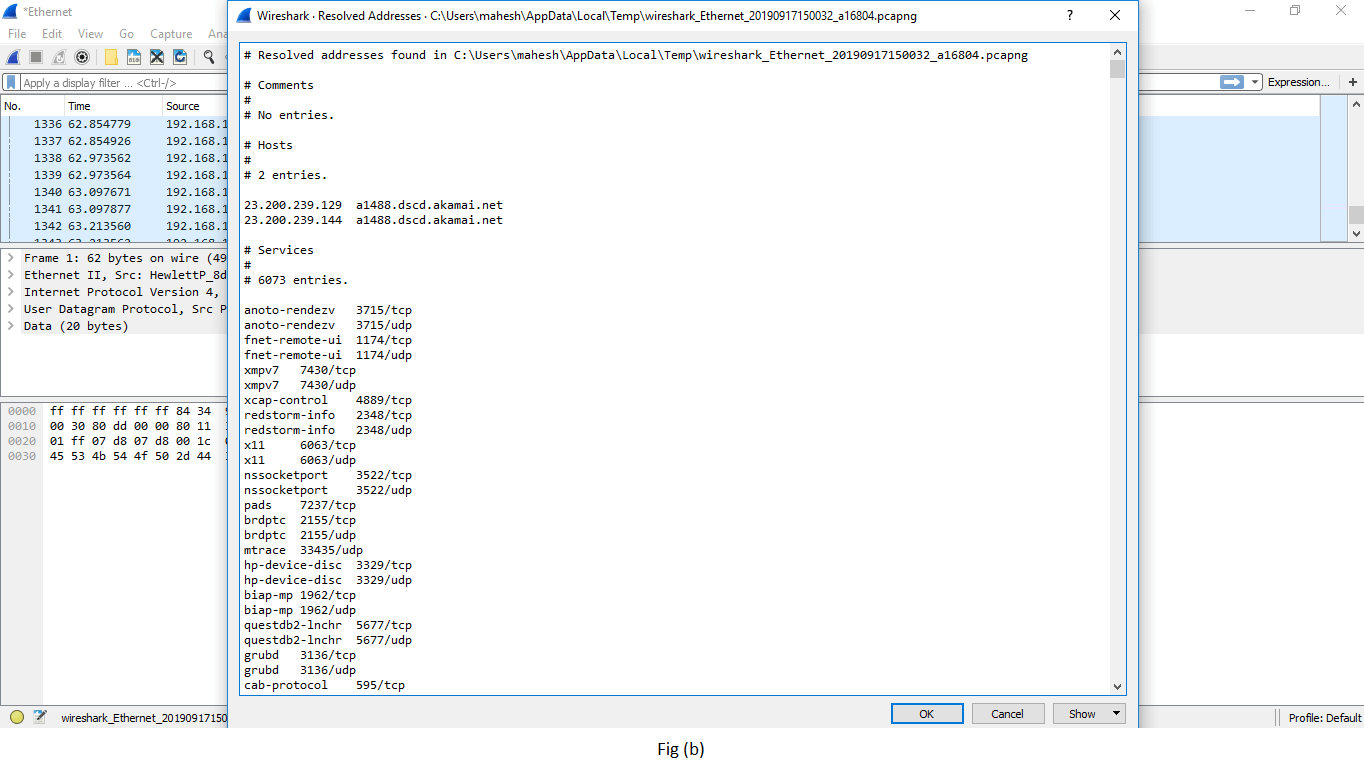
| Resolved addresses | This option includes all the types of the Top IP addresses and DNS that were resolved in your packet capture. It gives the thought of the different accessed resources during the bundle capture process. It is shown in fig (b). |
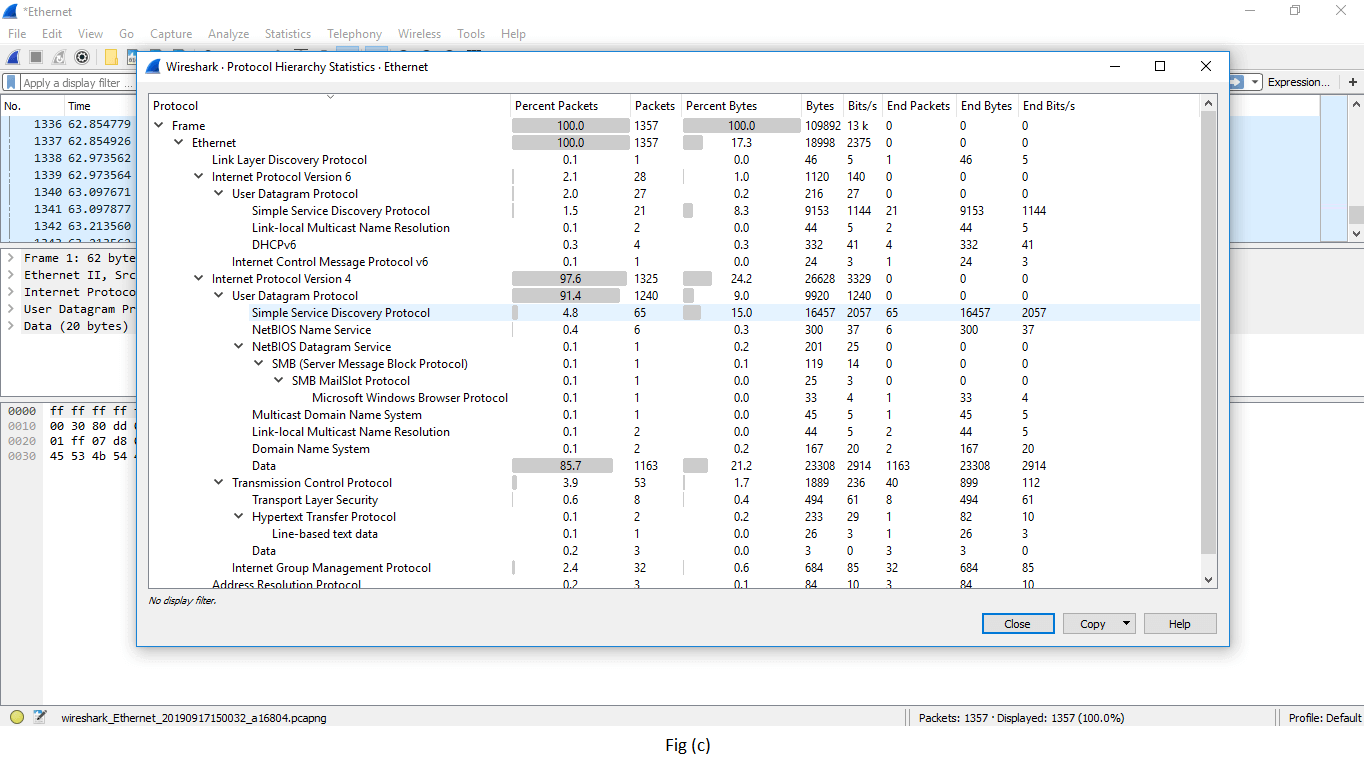
| Protocol hierarchy | Information technology is named equally the tree of all the protocols listed in the capture procedure. The image is shown to a higher place in fig (c). |
| Conversations | Each row of the listing gives the statistical value of a particular conversation. |
| Endpoints | Information technology is defined as a logical endpoint of the split up protocol traffic of the specified protocol layer. For example0 IP address volition send and receive all types of the parcel to the particular IP addresses. |
| Packet lengths | Information technology only displays the characteristics of unlike packets lengths determined in the network.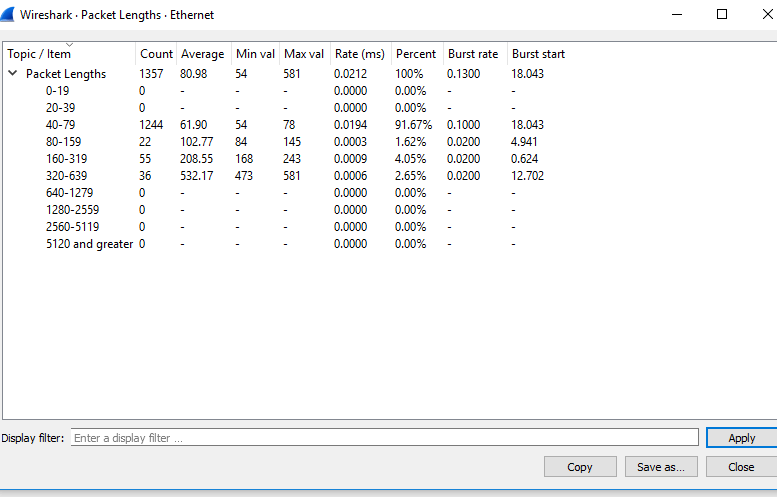 |
| I/O Graphs | It is the term used to display the graph of the captured packets. You lot can likewise apply filters during this process. The procedure is explained beneath in detail. |
| Service Response Time | It is the blazon of information which is available for many protocols. Information technology is defined as the time it takes between the request and the response time. The protocol for which this service is available are: AFP (Apple Filing Protocol) CAMEL DCE-RPC Bore FC (Fiber Channel) GTP (GPRS Tunneling Protocol) H.225 RAS LDAP (Lightweight Directory Admission Protocol) MEGACO MGCP (Media Gateway Command Protocol) NCP (NetWare Core Protocol) ONC-RPC RADIUS SCSI SMB (Server Message Block Protocol) SMB2 (Server Message Cake Protocol version 2) |
| DHCP (BOOTP) Statistics | Information technology is implemented as the option of BOOTP. DHCP is client/server protocol, dynamically used to assign IP addresses to a DHCP client. If DHCP does not work, then some computer organisation uses APIPA (Automatic Private IP Address) to assign the IP addresses. |
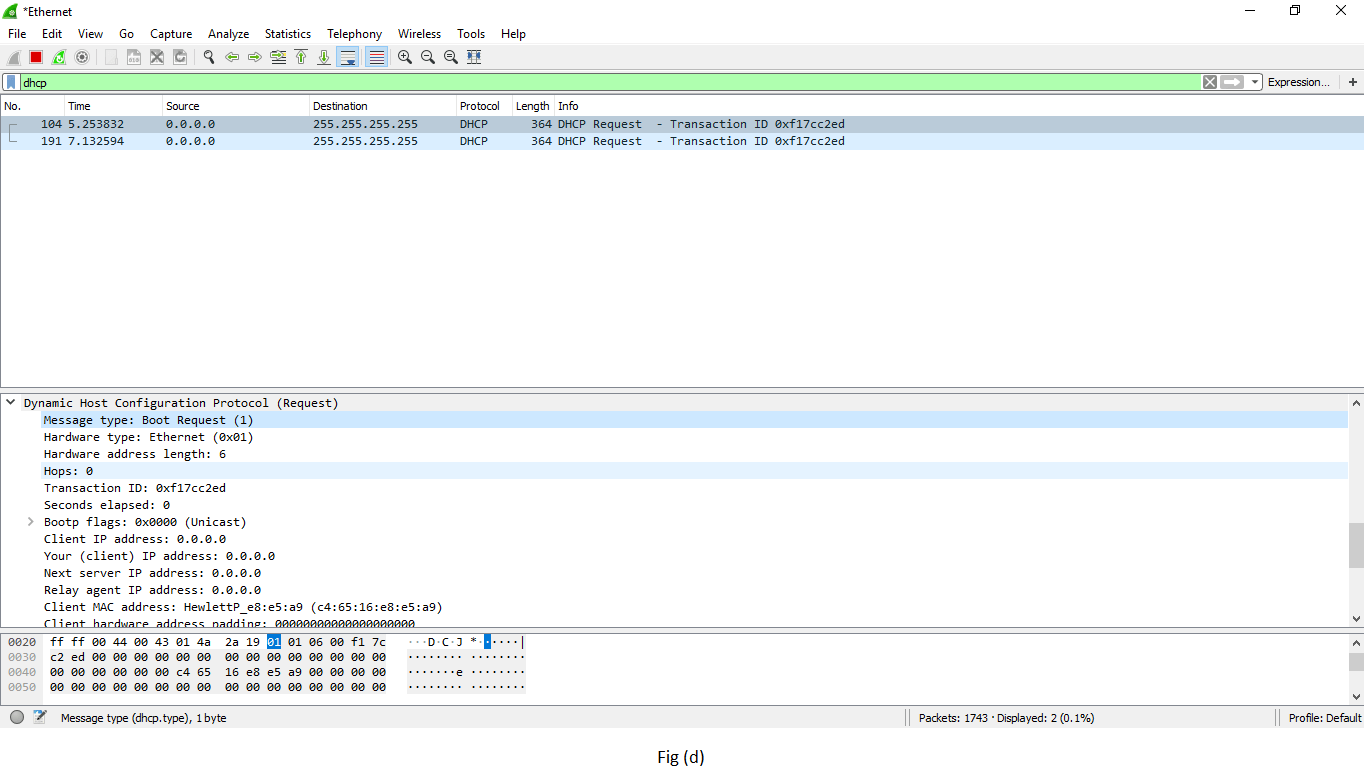
| ONC-RPC Programs | Information technology stands for Open Network Computing- Remote Procedure Call. It can utilise TCP and UDP as its transport protocol. ONC-RPC cannot be applied directly to filter in a capture process, but you can use TCP or UDP to filter on that i. It is shown in fig (d). |
| 29West | It is defined as ULLM technology. It stands for Ultra-Low Latency Messaging. |
| ANCP | Information technology stands for Access Node Control Protocol. Information technology is an L2CP (Layer 2 Control Protocol) and a TCP based one. It has its adjacency layer which decides the messages commutation past the ANCP endpoints with the use of 'Capabilities.' |
| BACnet | It was designed particularly to run into the communication needs of control systems and building automation. Information technology is used for applications such as fire detecting systems, lite control, etc. It provides the construction to substitution information despite the detail building service information technology performs. |
| Collectd | Information technology is used to monitor the traffic on the specific TCP port. |
| DNS | It stands for Domain Name Server, which gives a detailed analysis of the DNS traffic. Information technology provides the list of the codes returned in DNS. You tin can too view the errors through the traffic. |
| Flow-graph | It is a method to check connections between the client and the server. It is an efficient style to verify the connections between two endpoints. It also assists u.s.a. with troubleshooting capabilities. |
| HART-IP | Information technology gives the detail for the response, request, publishes, and error packets. It stands for Highway Addressable Remote Transducer over IP stats. |
| HPFEEDS | It determines the 'payload size per aqueduct and Opcodes.' |
| HTTP | It has four options:
|
| HTTP2 | It is the HTTP version ii. |
| Sametime | It is used to analyze the slow network traffic when the server and client have the sametime. |
| TCP Stream Graphs | It is explained beneath in detail: |
| UDP Multicast Streams | Through this command, stream parameters and burst parameters tin exist ready. It includes OSPF, IGMP, and video streams. |
| F5 | It includes the virtual server distribution and the tmm distribution. It specifies the tcpdump commands. |
| IPv4 Statistics IPv6 Statistics | These options determine all addresses, destination and ports, IP protocol types, and the source and destination accost. |
I/O GRAPHS
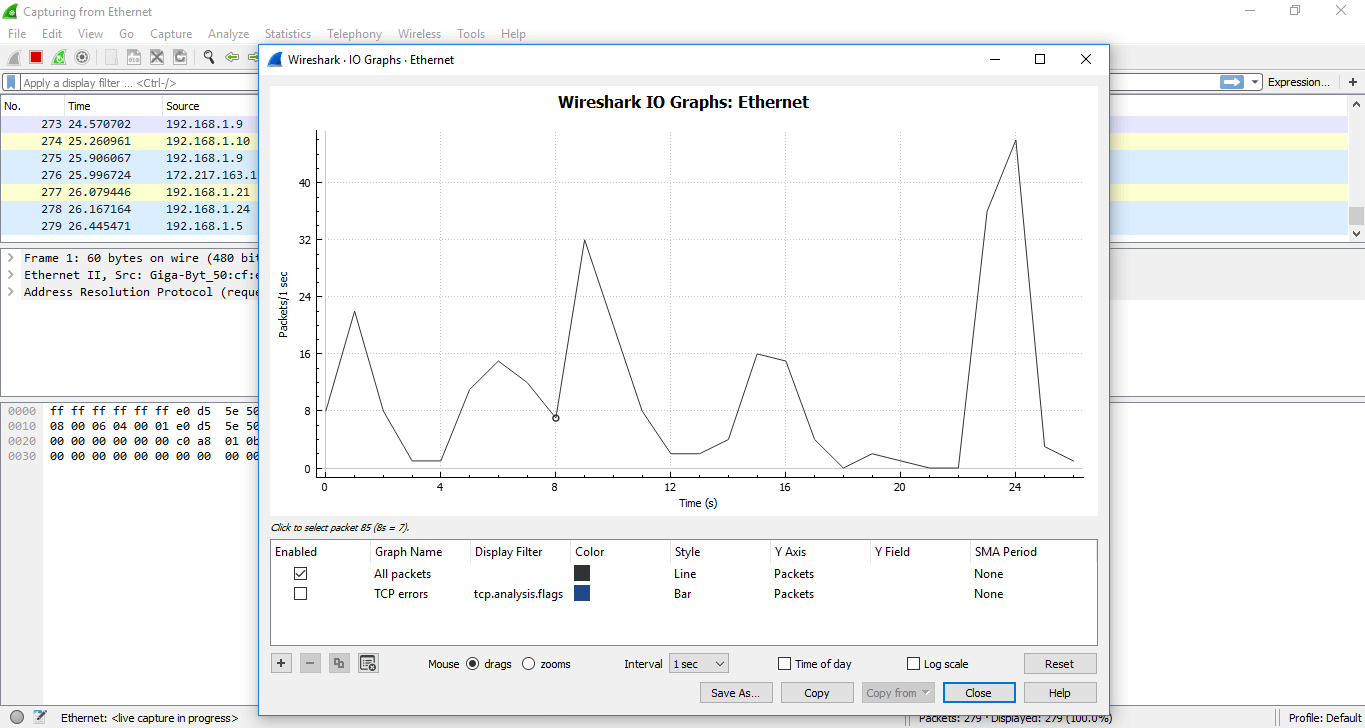
It shows the graph for the network traffic. The graph will wait similar but changes every bit per the traffic involved. There is a table below the effigy, which has some filters. Using the '+' sign, yous can add more filters and utilise '-sign you tin can remove the existing filters. You can also change the color. For every detail filter, yous tin add a colored layer, which increases the visibility of the graph.
The tick choice nether the 'Enabled,' displays the layer co-ordinate to your requirements.
For example, we have applied the filter 'TCP errors' and the changes can be viewed easily. The image is shown below:
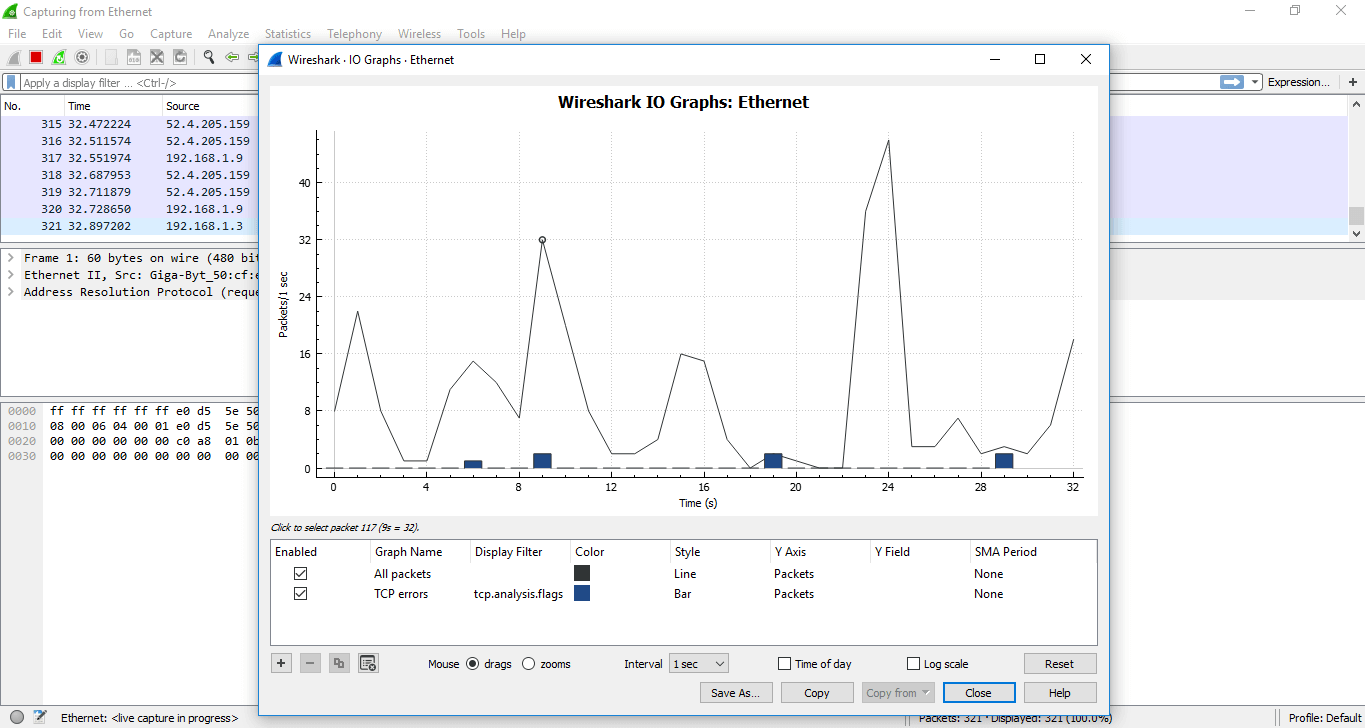
If you click on the particular point on the graph, you lot tin can lookout the corresponding packet will be shown on the screen of the network traffic. You tin also apply a filter on the particular port.
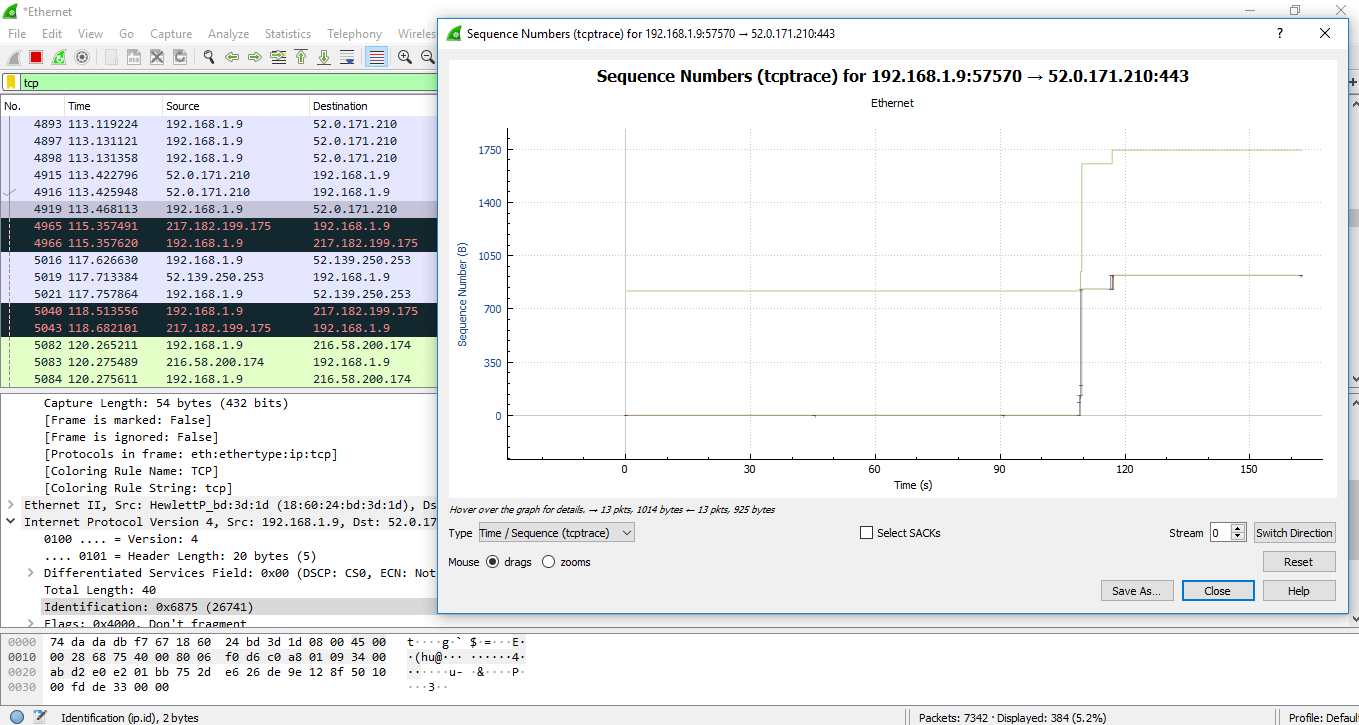
Some other category of the graph comes under the selection 'TCP Stream graphs.'
It gives the visualization of the TCP sequence number with time.
Below are the steps to understand the TCP Stream graphs:
- Open the Wireshark. Click on the interface to watch the network traffic.
- Utilize the filter as 'tcp.'
- Click on the pick 'Statistics 'on the menu bar and select 'TCP Stream graphs' and select 'Time sequence (tcptrace). You lot can also choose other options in the 'TCP Stream graphs' category depending on your requirements. At present the screen will await every bit:
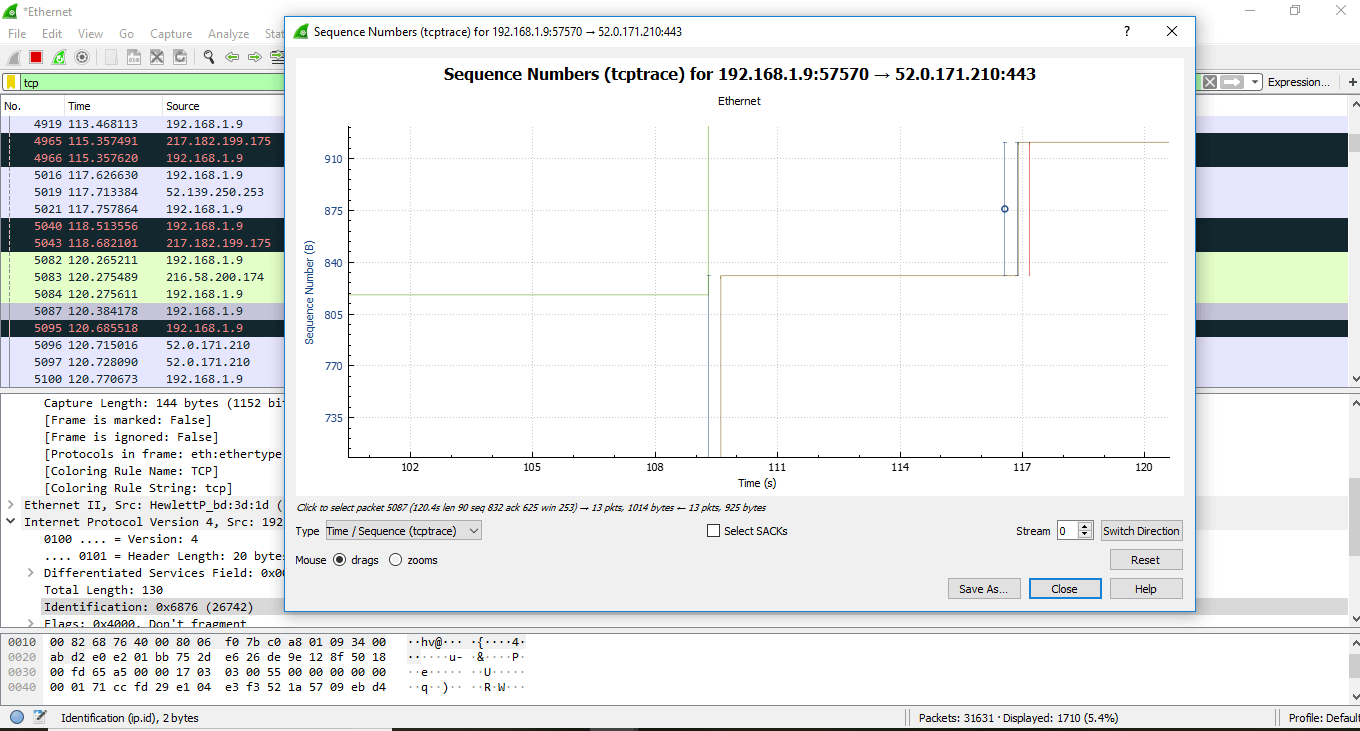
At present, as y'all zoom on the graph, you will detect the points in detail. The lines shown are the packets. The length along the Y-axis shows how big the bundle is. You can also run across the green line going upwards and then comes at the same level. This means that the data has been ACK (Best-selling). Here going up ways that more data is being sent.
The data is being sent and and then ACK, this is the proper use of the TCP. The apartment line here signifies that cipher is happening.
The greenish line above is called 'received window.' The gap between the received window and the bundle, defines how much space is in the received buffer.
FACTS Nearly WIRESHARK/ Of import STEPS/ MOST USED
Below are the facts or points implemented in existent life:
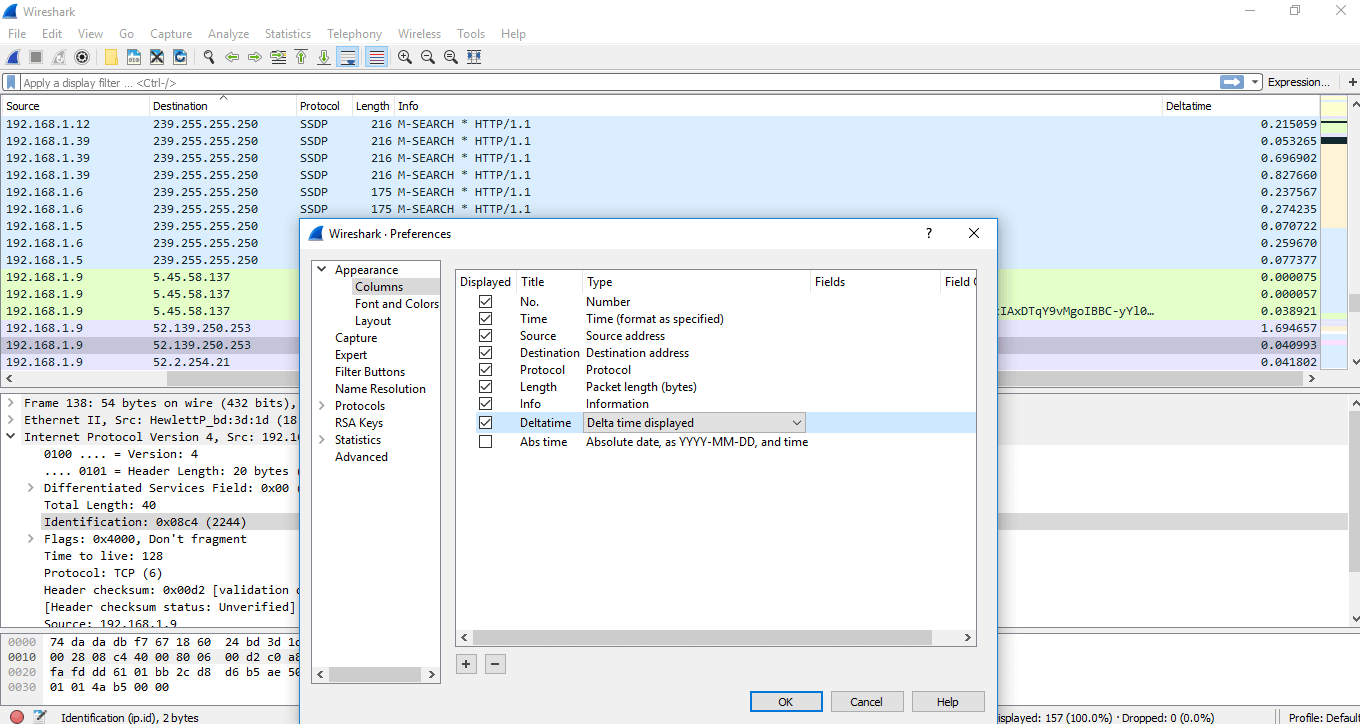
Adding a delta cavalcade: To add together any column, beneath are the steps:
- On whatever of the cavalcade menu, right-click and choose 'Column Preferences' then select 'Column.'
- Click on the '+' sign, and add the column by name like delta-time and under the 'Type' category, select the delta fourth dimension or delta time displayed.
- When y'all are capturing your information, analyze the trouble, you lot will get the three-mode handshake.
- It contains skillful options like the TCP options.
- From this, you can determine the shift time and figure out if you have captured packets on the client-side or the server-side. At that place is a piffling delay between SYN and SYN- ACK packet at server-side while there is a more than filibuster between the SYN and SYN-ACK at the client-side. There is a delay at the server-side only between the SYN-ACK and ACK. The SYN has to reach to the client. Later the three-way handshake, the data has to attain the server. Y
- ou can also discover the difference in the TCP options between the SYN and SYN-ACK packets. The window scaling factor is too essential, as shown below:
- One sequence number ways one byte of data. Information technology as well has an importance of the TCP Stream Graphs which is already explained to a higher place.
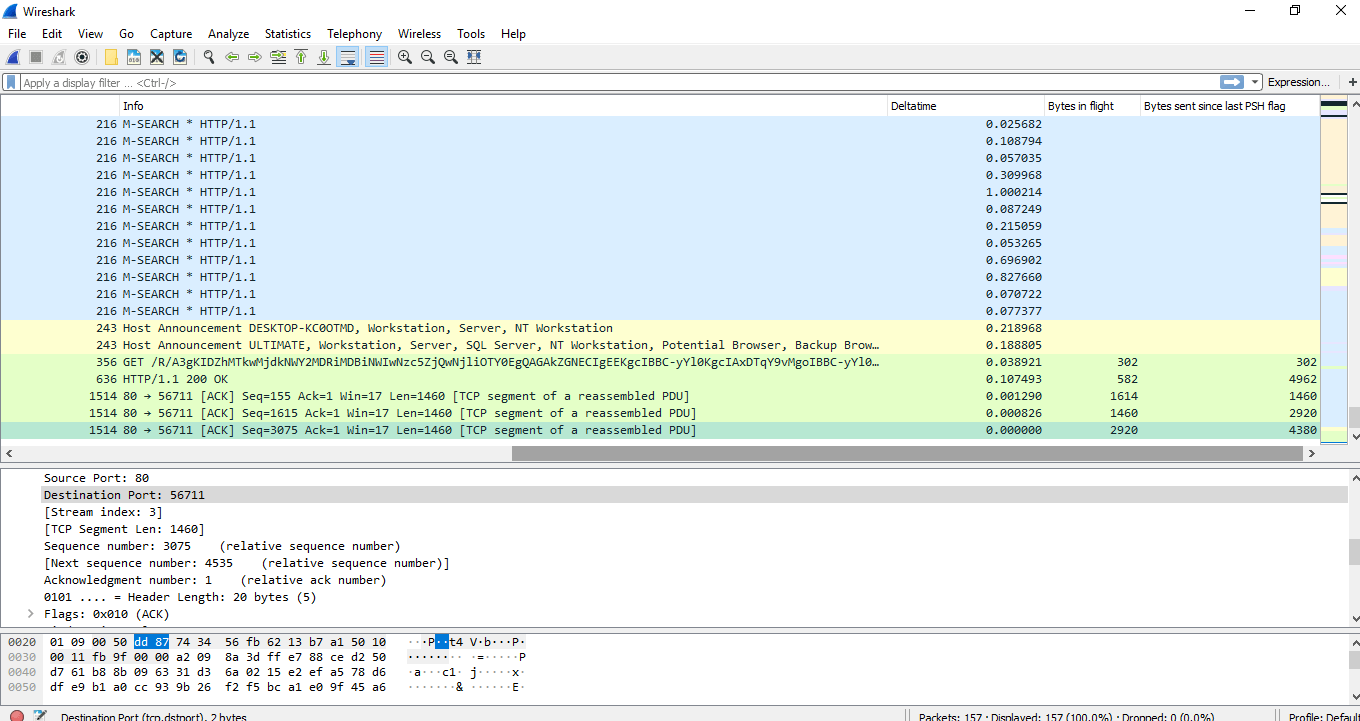
- Under the TCP options, capture window, you can come across the information about the 'PSH byte' and 'Bytes in flight.' Right-click on that and choose 'Apply every bit Cavalcade.' You can see both the columns and data according to information technology. The image for this is shown below:
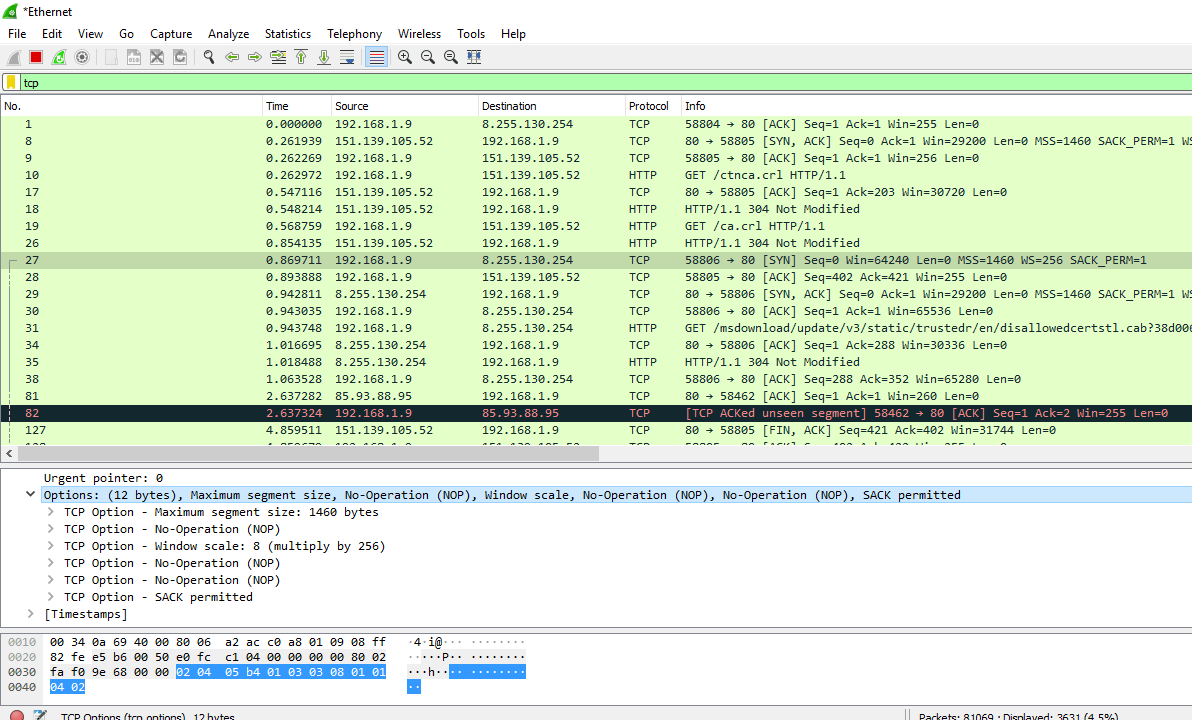
- In TCP Header, iii-fashion handshake MSS (Maximum Header Size) means that the maximum corporeality of data it can receive of TCP payload. The image is shown below:
- MSS 1460 implies that this is per bundle amount of data. This size varies from packet to packet. Something like a router, firewall, etc. will do MSS clamping considering it knows what is going frontward. It checks the value greater than 8000 bytes and brings down it to an appropriate level and then that it can go beyond without fragmentation or being dropped.
- The data with the 0 is the ax coming dorsum in the capture window. You can detect that the data and ACK are different at each bespeak. If we are on the acknowledgment side, we know that we have to send the ACK after two packets. A sender can ship X corporeality of packets depending on its congestion window. A sender can ship packets at once also. Afterwards the packets will go at the receiver and and then the acknowledgment comes back. The sender tin can send all packets before the ACK reaches information technology. If the buffer has less space left, then the sender has to send the packets co-ordinate to infinite. The ACK arrives on time, and if there is a delay in the ACK, syncing volition be delayed. So above information technology's, just a perspective example explained.
- We do recommend non to disable the default settings of the TCP and Wireshark unless yous know what you lot?re doing.
- If there are the bare page and slow loading, and then it is unusable.
- Information technology is proficient to capture packets from both ends.
- Lean on your provider when you have the data.
- Information technology is a Alive CAPTURE software used widely.
- It can also capture packets from a set of captured one'due south.
- There are many protocols dissectors.
- The listing of commonly used Endpoints or IP endpoints is: Bluetooth (MAC 48-bit addresses), Ethernet, fiber channel, USB, UDP, FDDI, IPv4, IPv6, JXTA, NCP, TCP, etc.
- Name resolutions are used to convert numerical values into the human-readable format. There are ii ways- network services resolution and resolve from Wireshark configuration files. Information technology is but possible when capturing is not in progress. Information technology can exist resolved subsequently the packet is added to the list. To rebuild the listing with correct resolved names you tin can use View-> Reload.
- In ARP, Wireshark asks the OS to convert the Ethernet address to the IP address.
- Since information technology is a live capture process, so information technology is of import to set the correct time and zone on your reckoner.
- Open up the Wireshark and then select the detail interface every bit explained in a higher place.
- Go to the 'Edit' option and select the 'Preferences' pick.
- A dialogue will appear as shown below:
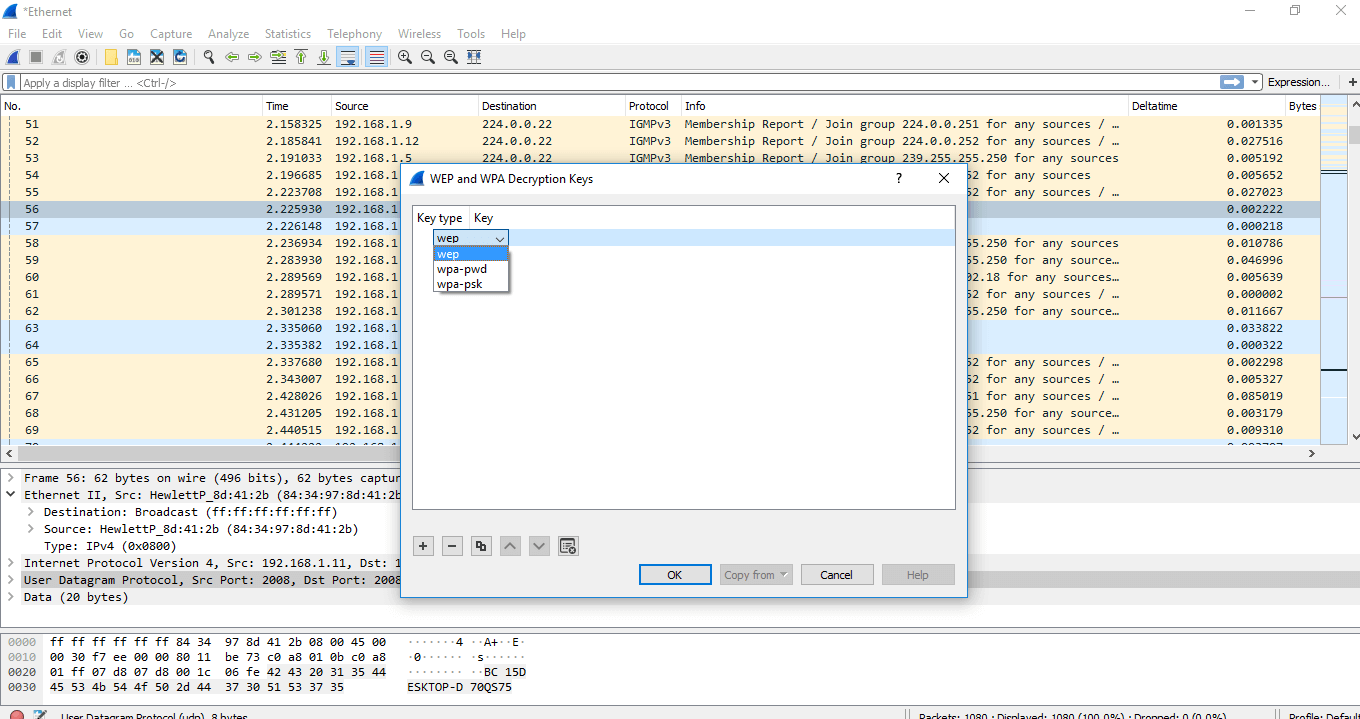
- Select the 'Protocol' choice in the left column.
- From the driblet-downward list, select the 'IEEE 802.11' option. Check the box of decryption and click on the Edit option under information technology.
- A box will appear. Click on the option shown below:
- Select the option wpa-pwd and set the countersign appropriately.
- The data will be decrypted.
- Only the above decryption process is simply possible if in that location is a proper handshake.
The screen will and so look as:
Beneath the captured packets, the data you run across in the square brackets is the data that is not available in the packet itself. It is something that Wireshark displays for your do good. If you lot want to add together anything from this screen to the column area, you can right-click and select 'Apply as cavalcade.' That option will exist added to the capture screen.
The most of import is:
3 Way-Handshake
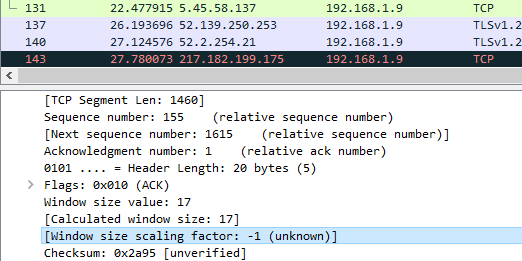
Without iii-manner handshake, you cannot view the window scaling factor.
Some Facts about Wireshark:
TELEPHONY
The Telephony is the option on the menu bar. The paradigm is shown below:
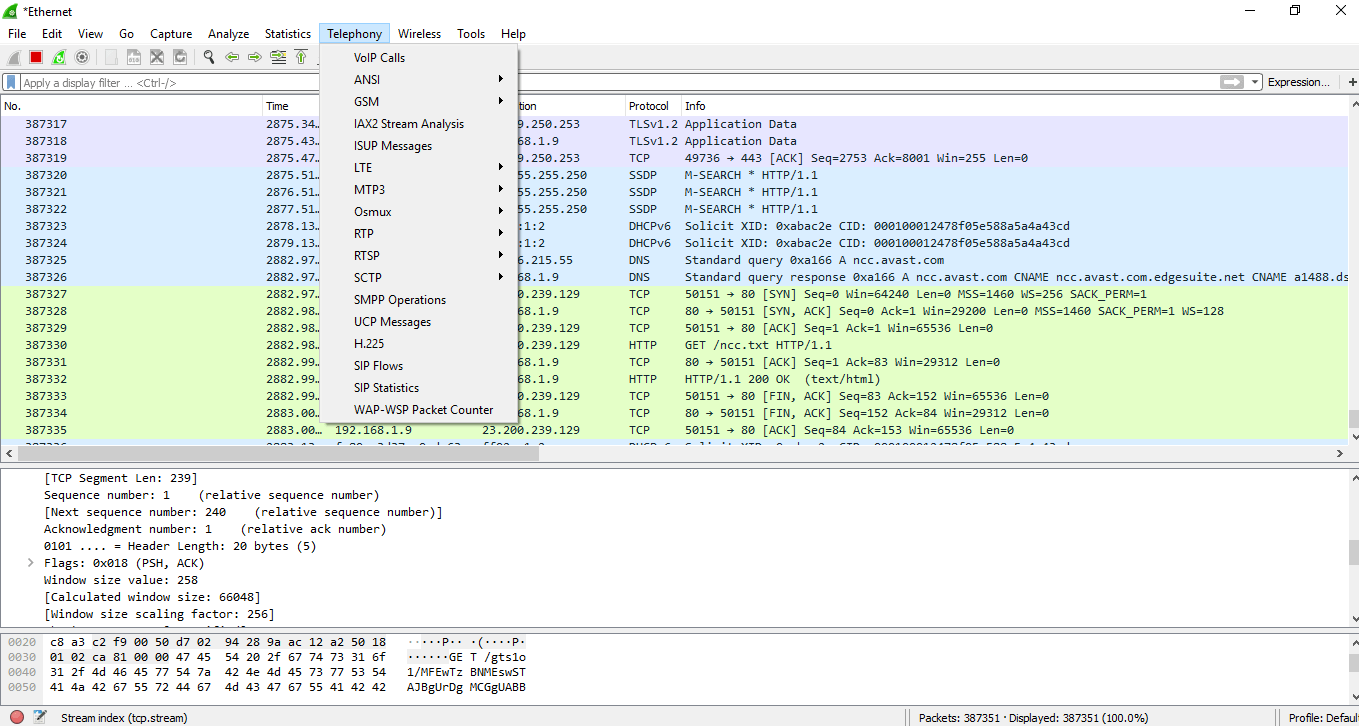
The options are explained beneath:
| VoIP calls | Information technology stands for Vox over Cyberspace Protocol. It gives the list of all the detected VoIP calls in the captured traffic. It shows the start time, stop time, initial speaker, protocol, elapsing, packet, state. |
| ANSI | Information technology stands for American National Standards Institute. ANSI standards are developed by organizations who are authorized by it. |
| GSM | It stands for Global System for Mobile. Information technology has various options. It has multiple options, which are used to view the messages count over the traffic. For this, you lot have to connect your phone to the calculator through the USB-TTL converter, verify the layer. After you have to load layer 1 Firmware into the osmocon. Run mobile and specify the interface for sending GSM TAP to heed to the interface through Wireshark. |
| IAX2 Stream Analysis | It shows the graph with the forward and the reverse streams. |
| ISUP Messages | It stands for ISDN User Parts. It is used to plant and release calls between telephone exchanges. It shows the letters by count and direction. |
| LTE | It stands for Long Term Evolution. It uses RRC (Radio Resource Control) protocol, which controls MAC and RLC layers in the LTE interface. It shows the statistics of the captured LTE MAC and LTE RLC traffic. |
| MTP3 | It provides messaging routing betwixt signaling points in the SS7 network. It shows its statistics and summary. It stands for Bulletin Transfer Part. |
| Osmux | It is a multiplex protocol, which reduces the bandwidth by substituting the vocalization and signaling traffic. If it is not detected then Wireshark display this information of Osmux on UDP packets or menstruum. |
| RTP | Information technology is called every bit RTP streams. Information technology starts with the sequence number, packet number, and further stats are created based on the jitter, bundle size, arrival time, and delay. Information technology stands for Existent-time Transport Protocol. |
| RTSP | It stands for Real-Time Streaming Protocol. It provides information about the package counter of response packets and requests packets. |
| SCTP | It stands for Stream Command Transmission Protocol. It is designed to transmit PSTN signaling letters over IP networks. It is only applicative for broader applications. |
| SMPP Operations | Information technology stands for Short Letters Peer to Peer. It determines the response, request, and operations of SMPP. |
| UCP Messages | It is used to determine whether the captured packet is UCP or Nacks. |
| H.225 | It is a streamed packetization and signaling protocol used for parcel-based multimedia communication systems. |
| SIP Flows | It stands for Session Initiation Protocol. At that place is no need for any regular connection or multiples lines. Instead, it is installed on your current cyberspace connection. It works with VoIP. |
| SIP Statistics | Information technology gives information about the request methods and all of the SIP requests over a connexion. |
| WAP-WSP Packet Counter | WSP stands for Wireless Session Protocol. It indicates the packets counts for all the Extended post methods, status codes, and PDU types. WAP uses brusque letters as a carrier. |
WIRESHARK DECRYPTION
The decryption process is used for the data to exist in a readable format. Below are the steps for the decryption process.
What Is Wireshark Used For,
Source: https://www.javatpoint.com/wireshark
Posted by: mirelesbobst1939.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Is Wireshark Used For"
Post a Comment