Carbon And Hydrogen Covalent Bond
Covalent Bonding (IGCSE)
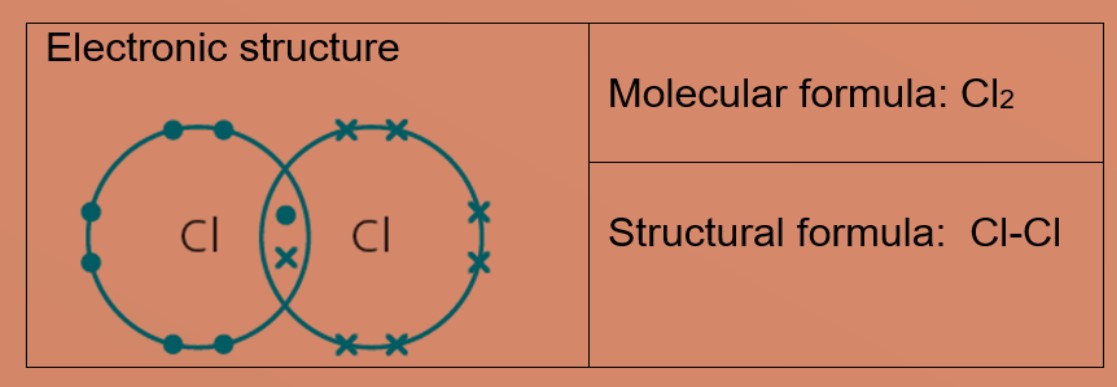
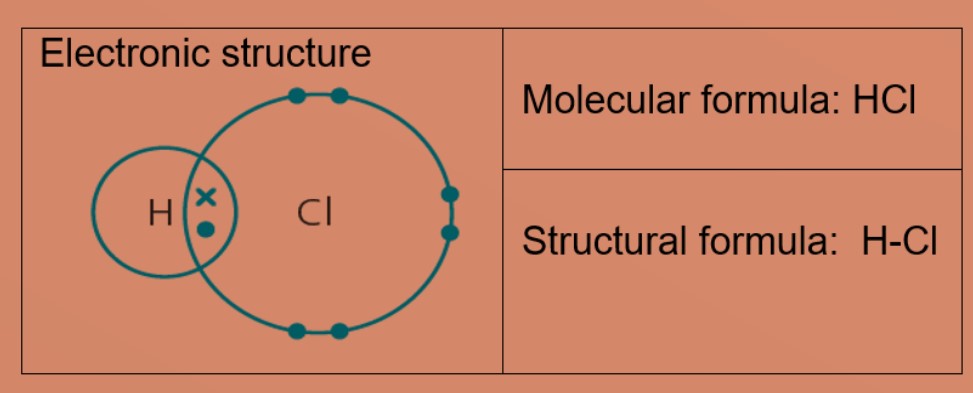
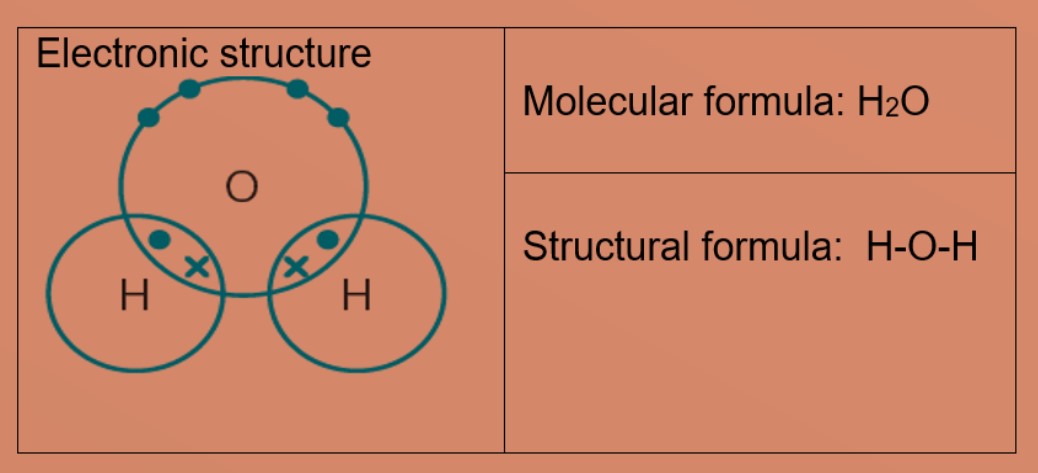
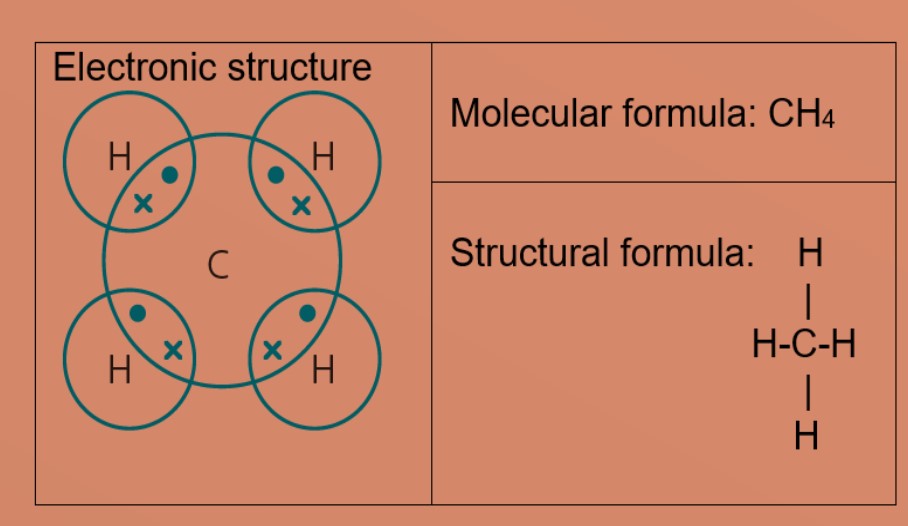
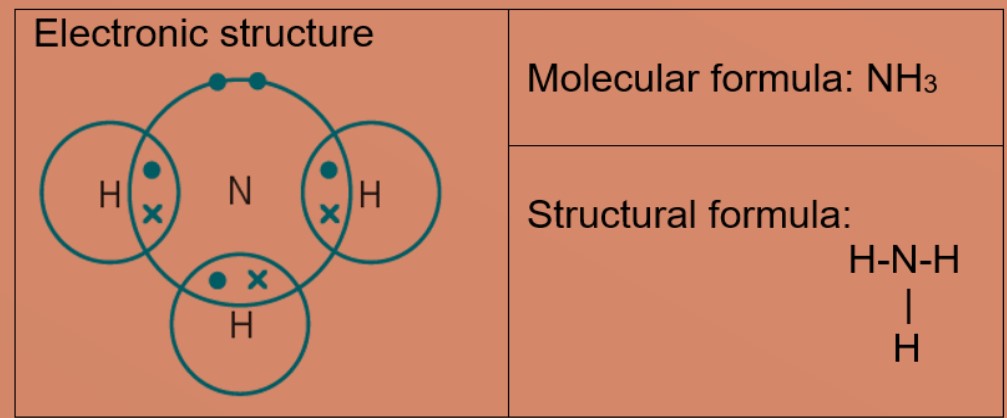
Molecules and Covalent bonds A covalent bond is formed when atoms share electrons. Eg 1: Hydrogen A hydrogen atom has just ane electron in the first trounce. Each hydrogen atom needs one more electron to exist stable. Ii hydrogen atoms tin can share one electron with each other to achieve stable electronic configuration for the first electron vanquish. Eg 2: Chlorine, molecular formula: Cl2 A chlorine atom has 7 valence electrons. Each chlorine atom needs 1 more electron to be stable. 2 chlorine atoms tin share one electron with each other to achieve stable electronic configuration for the valence electron shell. Eg 3 : Hydrogen chloride Each chlorine and hydrogen atom need 1 more than electron to exist stable. The chlorine atom and hydrogen atom share i electron with each other. Chlorine and hydrogen and so volition accept a stable electronic configuration of 2.8.8 and two respectively. Eg 4 : Water Oxygen atom needs 2 more than electrons and hydrogen atom need i more electron to exist stable. The oxygen cantlet shares two valence electrons with the ii hydrogen atoms. Each hydrogen cantlet shares one electron with oxygen atom. Oxygen and hydrogen have a stable electronic configuration of 2.eight and 2 respectively. Eg 4: Marsh gas Carbon atom needs 4 more than electrons to be stable. The carbon atom shares 4 valence electrons with 4 hydrogen atoms. Each hydrogen atom shares one electron with carbon atom. Carbon and hydrogen have a stable electronic configuration of 2.8 and 2 respectively. Eg 5: Ammonia Nitrogen atom needs 3 electron more to be stable. Nitrogen atom shares 3 valence electrons with 3 hydrogen atoms. Each hydrogen atom shares i electron with nitrogen atom. nitrogen and hydrogen have a stable electronic configuration of 2.eight and 2 respectively. • Depict the differences in volatility, solubility and electrical electrical conductivity between ionic and covalent compounds
Core
• Describe the formation of single covalent bonds in H2, Cfifty 2, H2O, CH4, NH3 and HCl as the sharing of pairs of electrons leading to the noble gas configuration.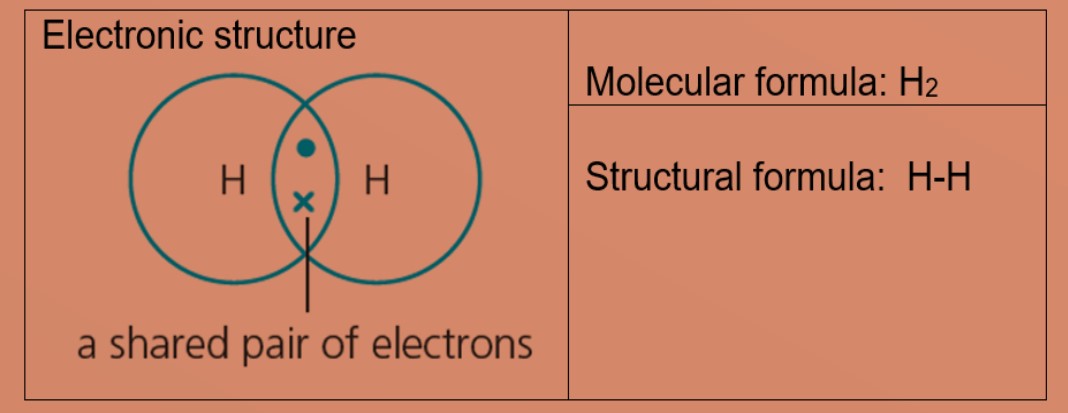
| Ionic chemical compound | Covalent compounds |
| Particles are ions | Particles are molecules |
| High melting and humid points due Giant ionic lattice structure with strong ionic bonds. Big amount of free energy is needed to interruption these bonds. | Low melting and boiling points due to Simple molecular construction with weak intermolecular forces. Small corporeality of free energy is needed to overcome these forces. |
| Usually soluble in h2o, insoluble in organic solvents | Usually insoluble in water, soluble in organic solvents |
| Conduct electricity in molten and aqueous state due to mobile ions, do not conduct in solid country | Usually exercise non carry electricity as there are no charged particles, no mobile ions or electrons |
Eg 1: Nitrogen A nitrogen atom has five valence electrons, it needs 3 more electrons to be stable. Eg 2: Ethene A carbon atom has four valence electrons, it needs four more electrons to exist stable. Eg3: Methanol A carbon atom has four valence electrons, it needs 4 more electrons to be stable. Oxygen cantlet has half-dozen valence electrons and needs 2 more valence electrons to be stable. The carbon atom shares iii valence electrons with 3 hydrogen atoms and 1 valence electron with one oxygen cantlet. Oxygen cantlet will share 2 valence electrons, one with carbon and i with hydrogen. This results in hydrogen atoms having 2 valence electrons in commencement shell and carbon and oxygen has eight valence electrons each. Eg4: Carbon dioxide A carbon cantlet has four valence electrons, information technology needs 4 more electrons to be stable. Oxygen atom has 6 valence electrons and needs 2 more valence electrons to be stable. The carbon atom shares all four valence electrons: two with each oxygen atom. Each oxygen atom volition share ii valence electrons with carbon atom, grade 2 double covalent bonds in the molecule. This results in carbon and oxygen has eight valence electrons each. • Explicate the differences in melting bespeak and boiling bespeak of ionic and covalent compounds in terms of attractive forces Ionic compounds have high melting and humid points due giant ionic lattice structure with strong ionic bonds (electrostatic forces of attraction between positively charged ions). Large amount of free energy is needed to suspension these strong bonds.
Supplement
• Describe the electron system in more complex covalent molecules such as Nii, CtwoHfour, CHiiiOH and CO2
Two nitrogen atoms share three electrons each, forming triple covalent bonds in the molecule with the formula Due northtwo. Each atom now has eight valence electrons and is stable.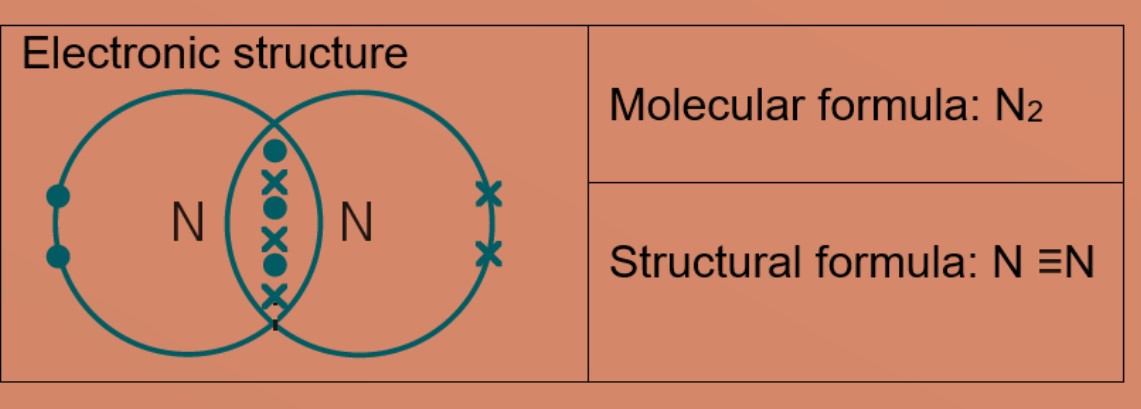
Hydrogen atom needs one more than electron to be stable and carbon atoms will share two valence electrons with 2 hydrogen atoms. After sharing two valence electrons with hydrogen atoms to form single covalent bond, each carbon cantlet at present needs two more valence electrons and share two valence electrons with each other to grade double covalent bonds between two carbon atoms. This results in hydrogen atoms having 2 valence electrons in first shell and carbon has eight valence electrons.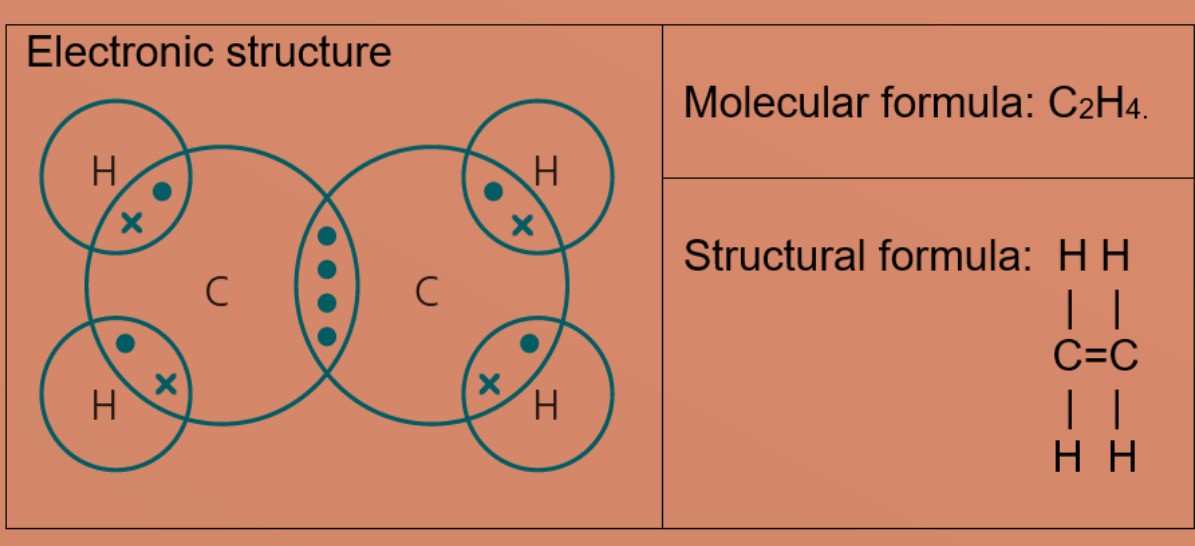
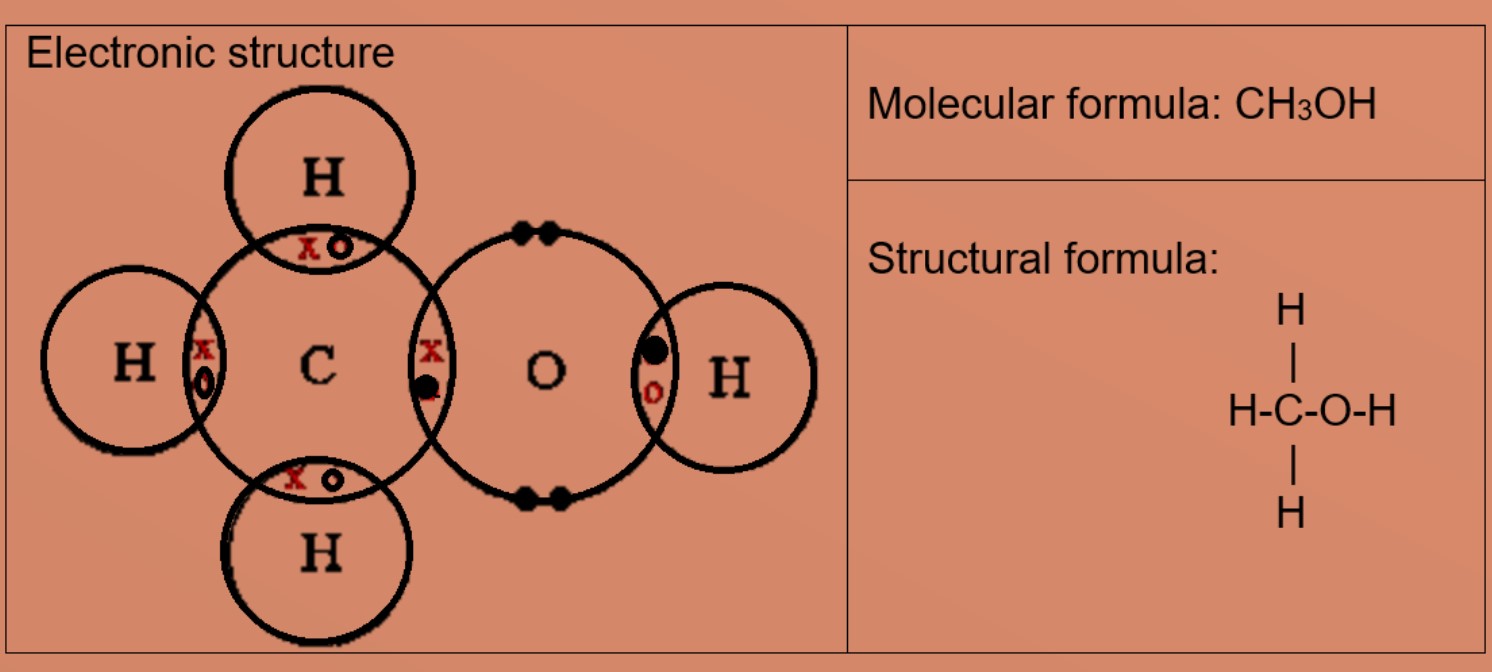
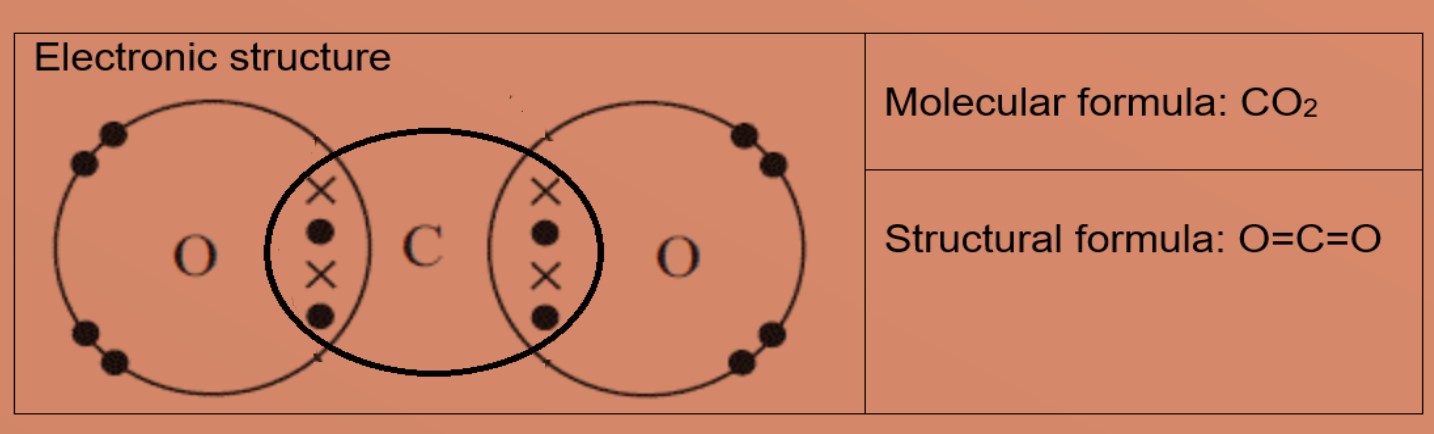
Covalent compounds commonly take low melting and boiling point due to simple molecular structure with weak intermolecular forces. Minor amount of energy is needed to overcome these weak forces.
Carbon And Hydrogen Covalent Bond,
Source: https://misschen.com.sg/Article-detail/9/covalent-bonding-and-molecules
Posted by: mirelesbobst1939.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Carbon And Hydrogen Covalent Bond"
Post a Comment